Takes a series of key frame camera positions and smoothly interpolates between them. Generates a data.frame that can be passed to `render_animation()`.
generate_camera_motion(
positions,
lookats = NULL,
apertures = 0,
fovs = 40,
focal_distances = NULL,
ortho_dims = NULL,
camera_ups = NULL,
type = "cubic",
frames = 30,
closed = FALSE,
aperture_linear = TRUE,
fov_linear = TRUE,
focal_linear = TRUE,
ortho_linear = TRUE,
constant_step = TRUE,
curvature_adjust = "none",
curvature_scale = 30,
offset_lookat = 0,
damp_motion = FALSE,
damp_magnitude = 0.1,
progress = TRUE
)Arguments
- positions
A list or 3-column XYZ matrix of camera positions. These will serve as key frames for the camera position. Alternatively, this can also be the a dataframe of the keyframe output from an interactive rayrender session (`ray_keyframes`).
- lookats
Default `NULL`, which sets the camera lookat to the origin `c(0,0,0)` for the animation. A list or 3-column XYZ matrix of `lookat` points. Must be the same number of points as `positions`.
- apertures
Default `0`. A numeric vector of aperture values.
- fovs
Default `40`. A numeric vector of field of view values.
- focal_distances
Default `NULL`, automatically the distance between positions and lookats. Numeric vector of focal distances.
- ortho_dims
Default `NULL`, which results in `c(1,1)` orthographic dimensions. A list or 2-column matrix of orthographic dimensions.
- camera_ups
Default `NULL`, which gives at up vector of `c(0,1,0)`. Camera up orientation.
- type
Default `cubic`. Type of transition between keyframes. Other options are `linear`, `quad`, `bezier`, `exp`, and `manual`. `manual` just returns the values passed in, properly formatted to be passed to `render_animation()`.
- frames
Default `30`. Total number of frames.
- closed
Default `FALSE`. Whether to close the camera curve so the first position matches the last. Set this to `TRUE` for perfect loops.
- aperture_linear
Default `TRUE`. This linearly interpolates focal distances, rather than using a smooth Bezier curve or easing function.
- fov_linear
Default `TRUE`. This linearly interpolates focal distances, rather than using a smooth Bezier curve or easing function.
- focal_linear
Default `TRUE`. This linearly interpolates focal distances, rather than using a smooth Bezier curve or easing function.
- ortho_linear
Default `TRUE`. This linearly interpolates orthographic dimensions, rather than using a smooth Bezier curve or easing function.
- constant_step
Default `TRUE`. This will make the camera travel at a constant speed.
- curvature_adjust
Default `none`. Other options are `position`, `lookat`, and `both`. Whether to slow down the camera at areas of high curvature to prevent fast swings. Only used for curve `type = bezier`. This does not preserve key frame positions. Note: This feature will likely result in the `lookat` and `position` diverging if they do not have similar curvatures at each point. This feature is best used when passing the same set of points to `positions` and `lookats` and providing an `offset_lookat` value, which ensures the curvature will be the same.
- curvature_scale
Default `30`. Constant dividing factor for curvature. Higher values will subdivide the path more, potentially finding a smoother path, but increasing the calculation time. Only used for curve `type = bezier`. Increasing this value after a certain point will not increase the quality of the path, but it is scene-dependent.
- offset_lookat
Default `0`. Amount to offset the lookat position, either along the path (if `constant_step = TRUE`) or towards the derivative of the Bezier curve.
- damp_motion
Default `FALSE`. Whether to damp the motion of the camera, so that quick movements are damped and don't result in shakey motion. This function tracks the current position, and linearly interpolates between that point and the next point using value `damp_magnitude`. The equation for the position is `cam_current = cam_current * damp_magnitude + cam_next_point * (1 - damp_magnitude)`.
- damp_magnitude
Default `0.1`. Amount to damp the motion, a numeric value greater than `0` (no damping) and less than `1`.
- progress
Default `TRUE`. Whether to display a progress bar.
Value
Data frame of camera positions, orientations, apertures, focal distances, and field of views
Examples
#Create and animate flying through a scene on a simulated roller coaster
if(run_documentation()) {
set.seed(3)
elliplist = list()
ellip_colors = rainbow(8)
for(i in 1:1200) {
elliplist[[i]] = ellipsoid(x=10*runif(1)-5,y=10*runif(1)-5,z=10*runif(1)-5,
angle = 360*runif(3), a=0.1,b=0.05,c=0.1,
material=glossy(color=sample(ellip_colors,1)))
}
ellip_scene = do.call(rbind, elliplist)
camera_pos = list(c(0,1,15),c(5,-5,5),c(-5,5,-5),c(0,1,-15))
#Plot the camera path and render from above using the path object:
generate_ground(material=diffuse(checkercolor="grey20"),depth=-10) %>%
add_object(ellip_scene) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=50,radius=10,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
add_object(path(camera_pos, material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
render_scene(lookfrom=c(0,20,0), width=800,height=800,samples=16,
camera_up = c(0,0,1),
fov=80)
}
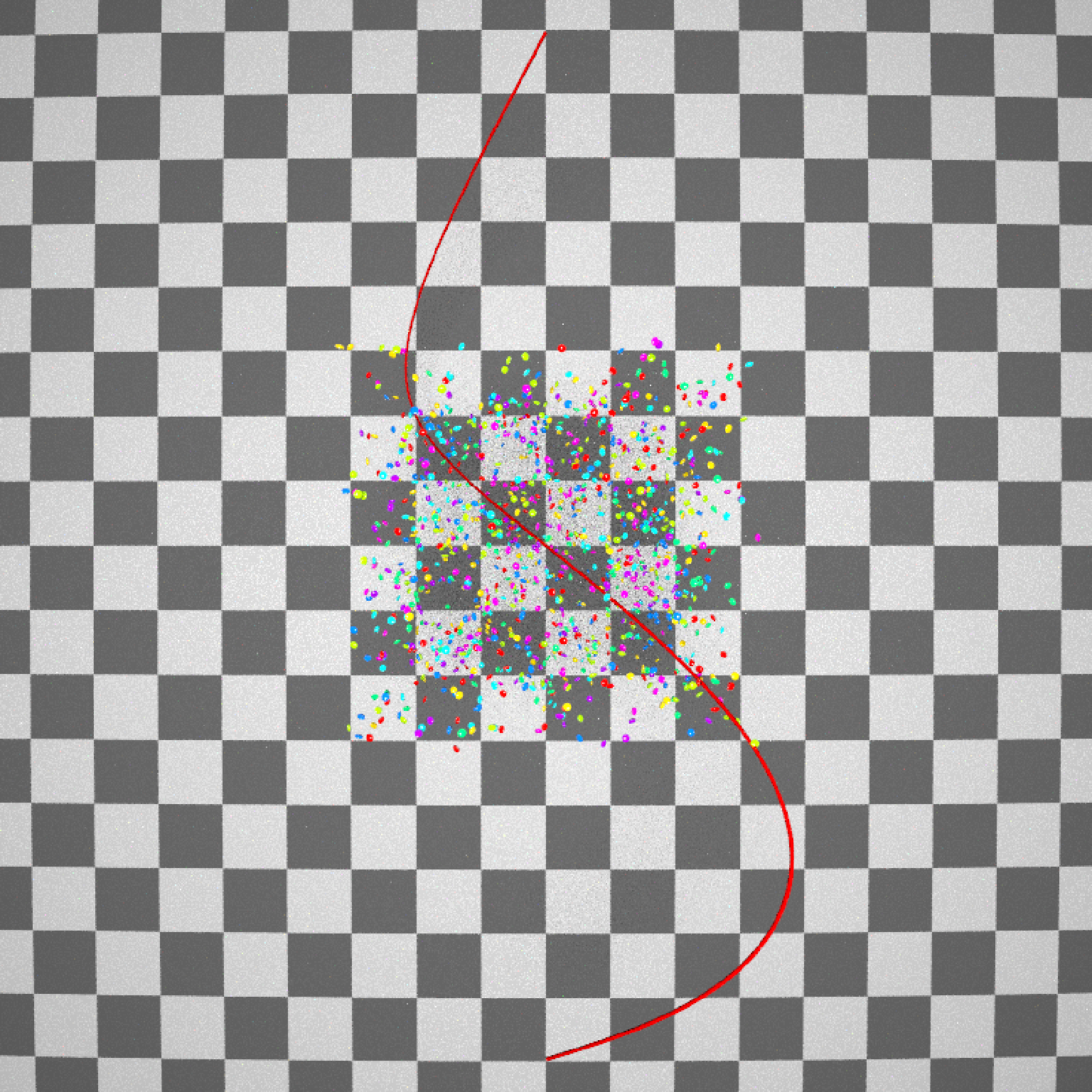 if(run_documentation()) {
#Side view
generate_ground(material=diffuse(checkercolor="grey20"),depth=-10) %>%
add_object(ellip_scene) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=50,radius=10,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
add_object(path(camera_pos, material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
render_scene(lookfrom=c(20,0,0),width=800,height=800,samples=16,
fov=80)
}
if(run_documentation()) {
#Side view
generate_ground(material=diffuse(checkercolor="grey20"),depth=-10) %>%
add_object(ellip_scene) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=50,radius=10,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
add_object(path(camera_pos, material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
render_scene(lookfrom=c(20,0,0),width=800,height=800,samples=16,
fov=80)
}
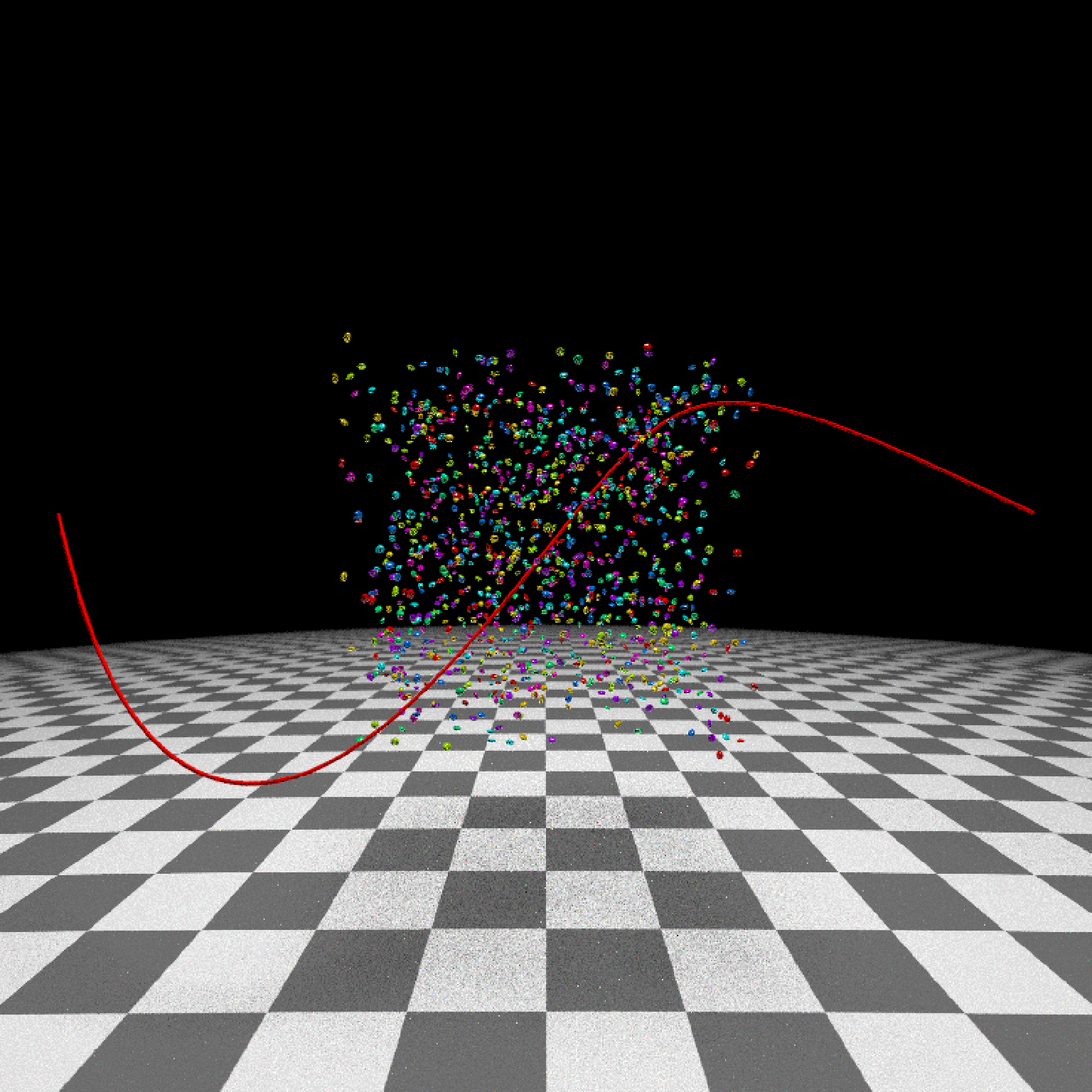 if(run_documentation()) {
#View from the start
generate_ground(material=diffuse(checkercolor="grey20"),depth=-10) %>%
add_object(ellip_scene) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=50,radius=10,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
add_object(path(camera_pos, material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
render_scene(lookfrom=c(0,1.5,16),width=800,height=800,samples=16,
fov=80)
}
if(run_documentation()) {
#View from the start
generate_ground(material=diffuse(checkercolor="grey20"),depth=-10) %>%
add_object(ellip_scene) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=50,radius=10,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
add_object(path(camera_pos, material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
render_scene(lookfrom=c(0,1.5,16),width=800,height=800,samples=16,
fov=80)
}
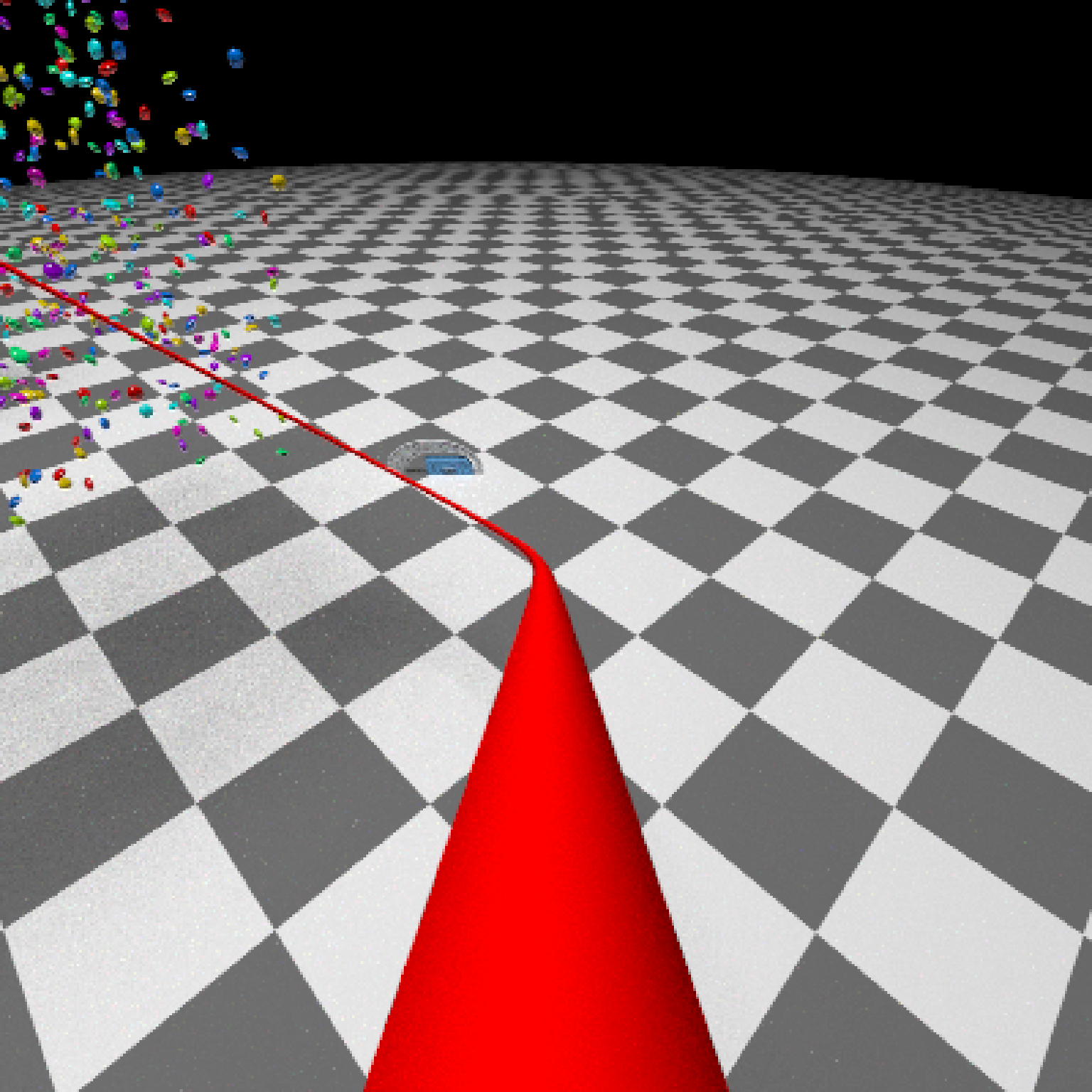
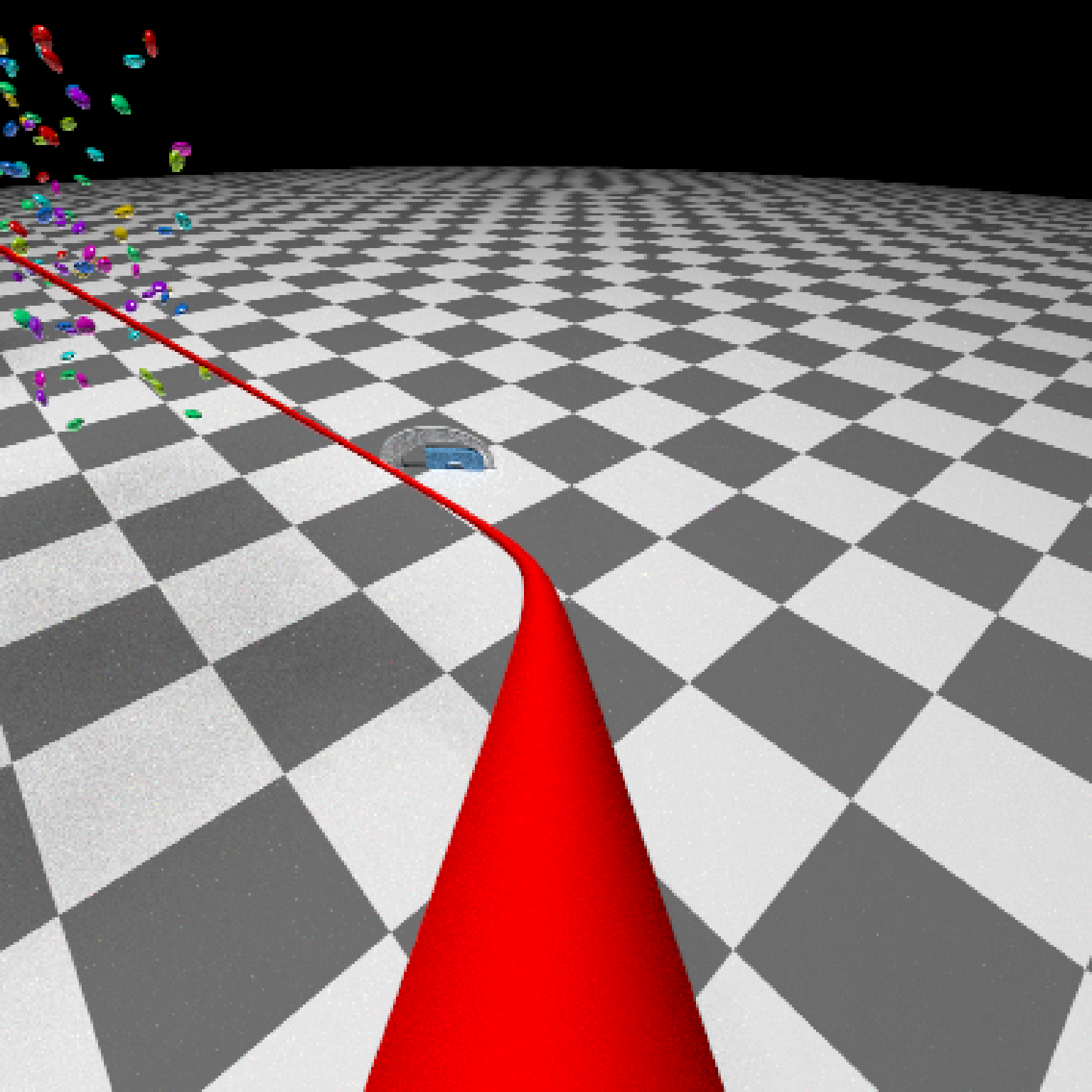
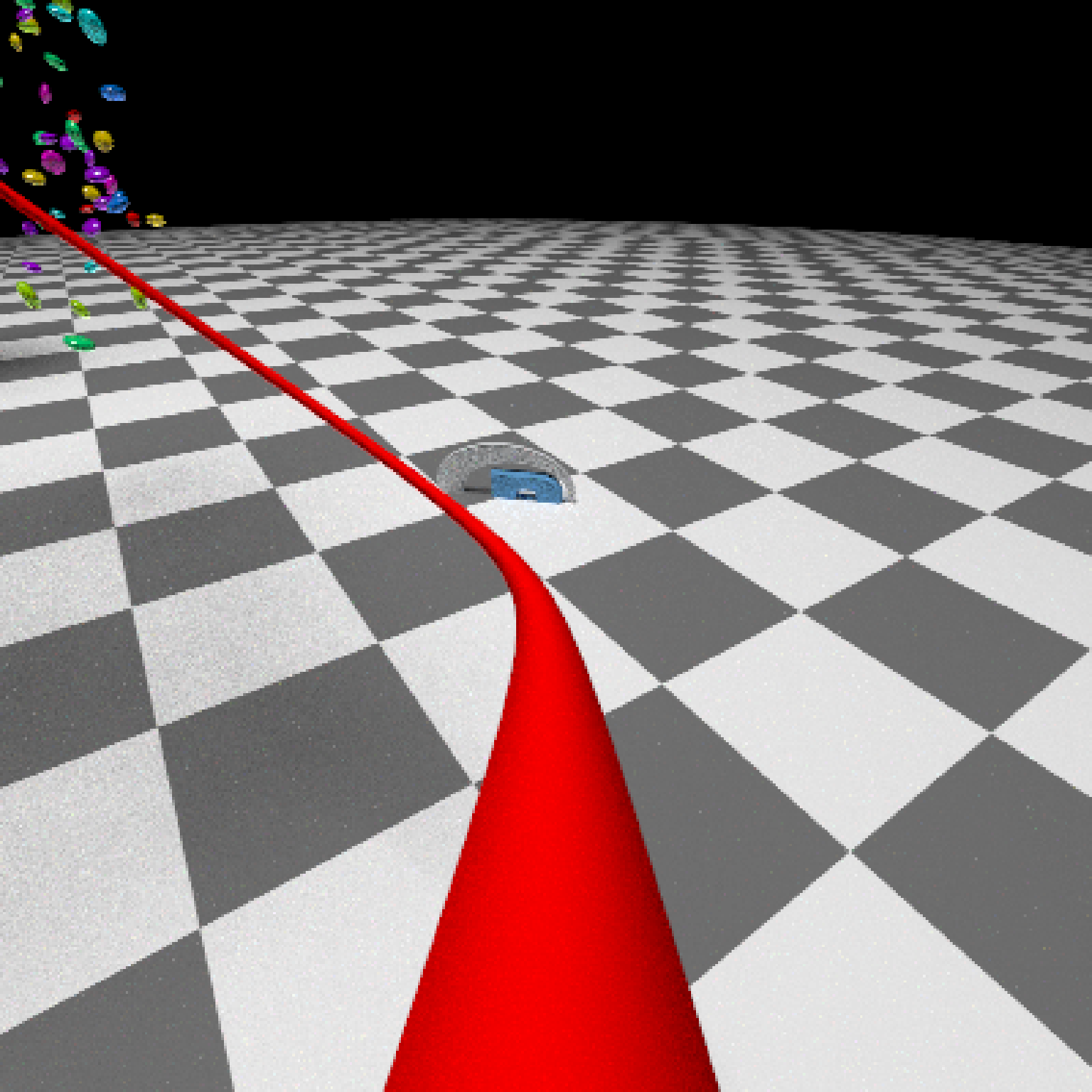
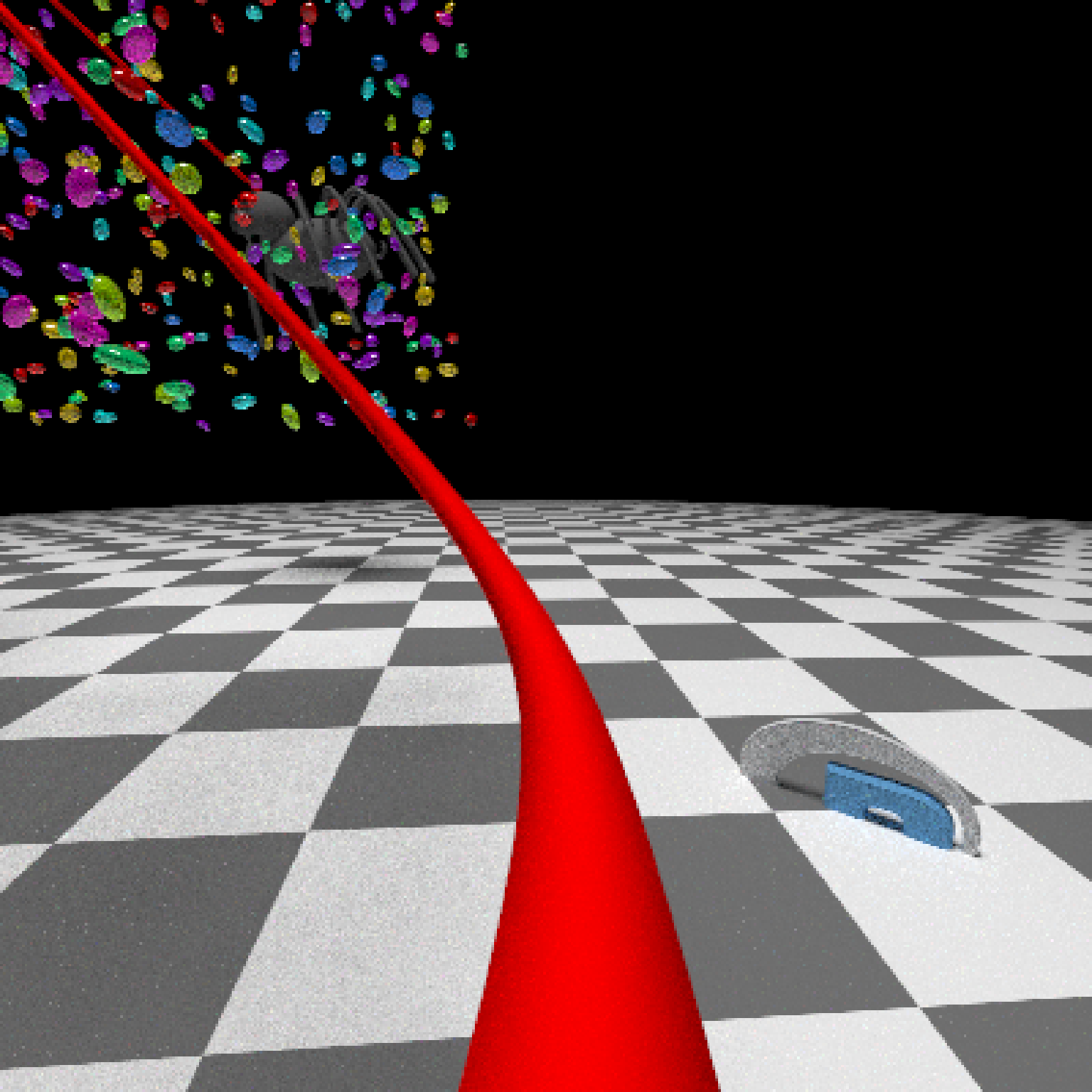
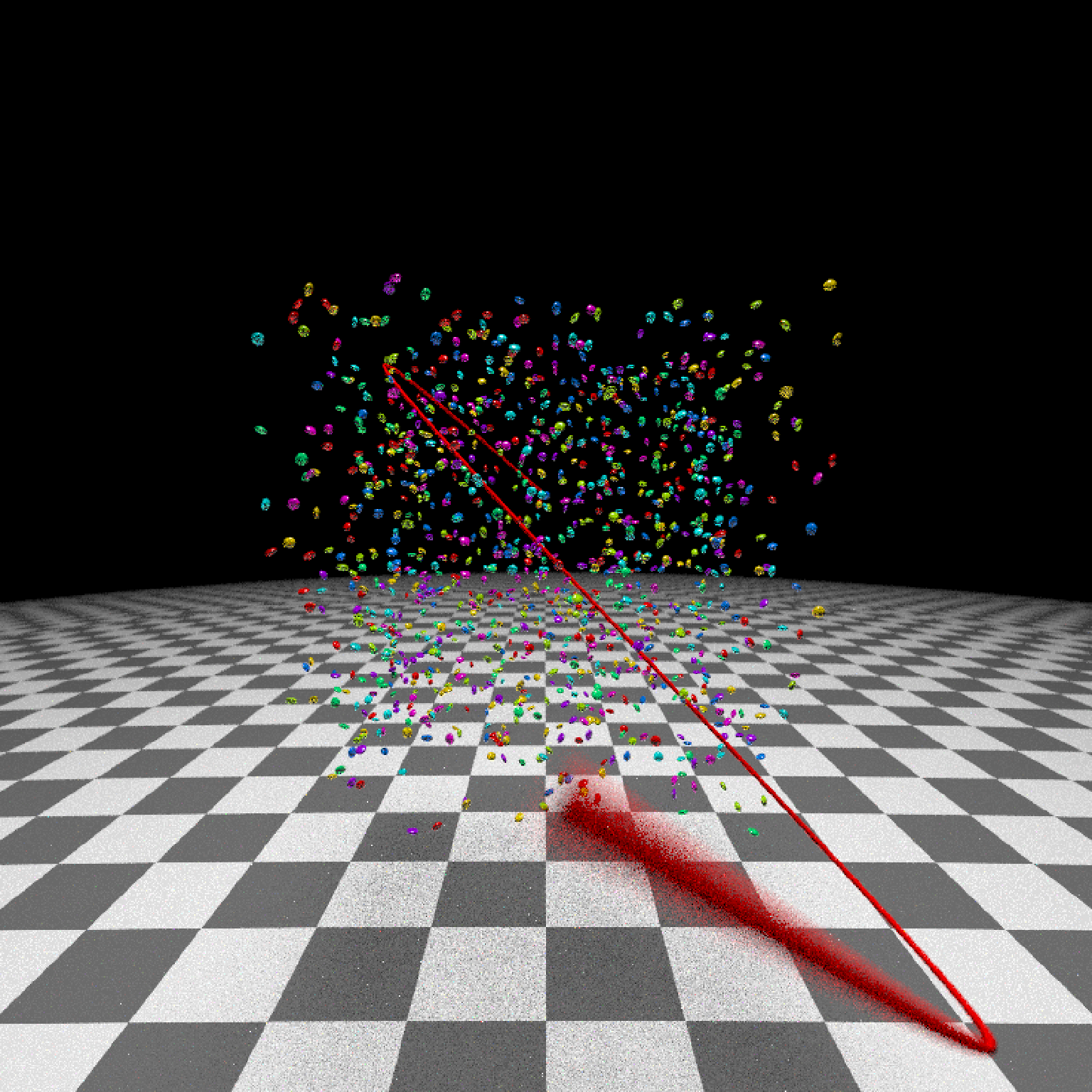 if(run_documentation()) {
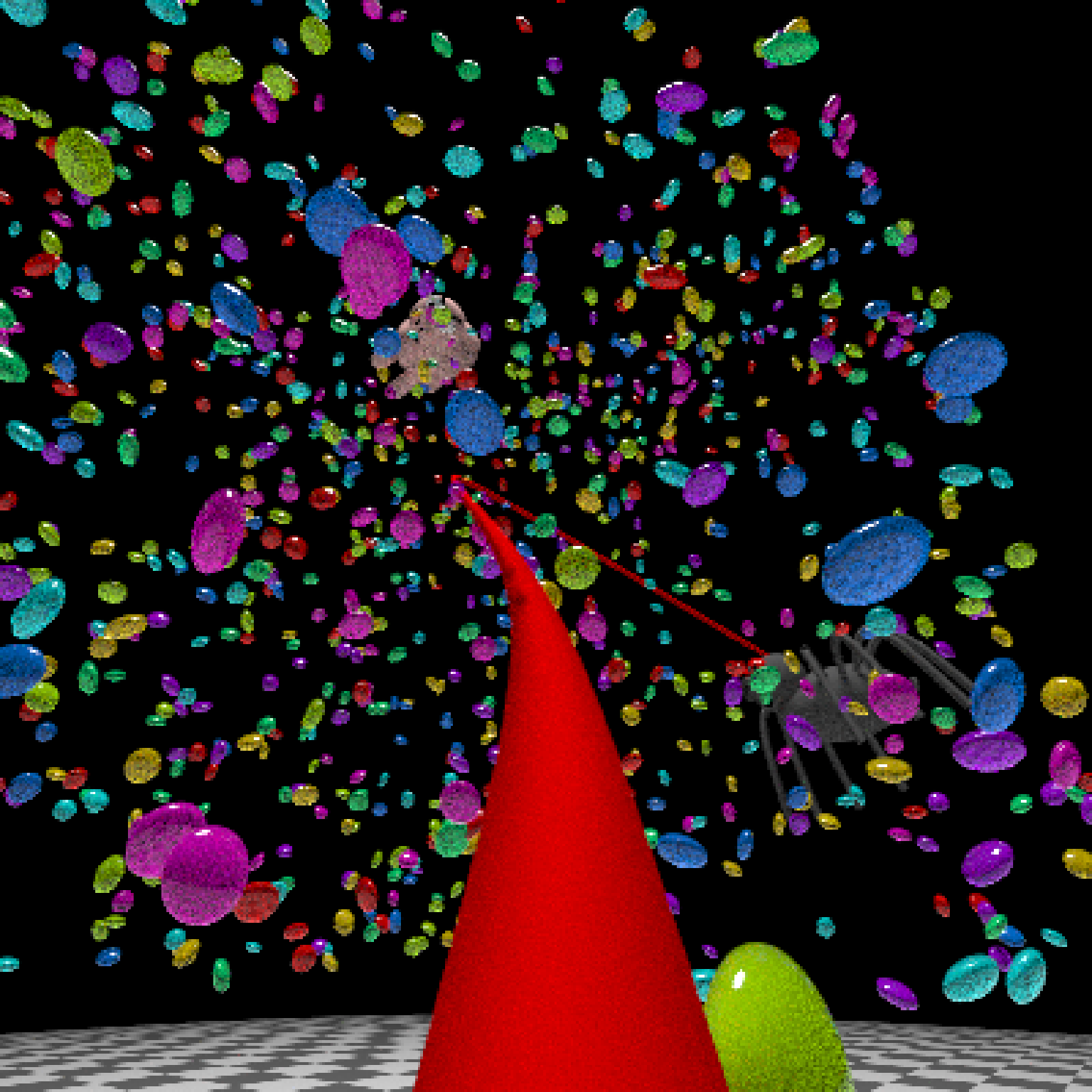
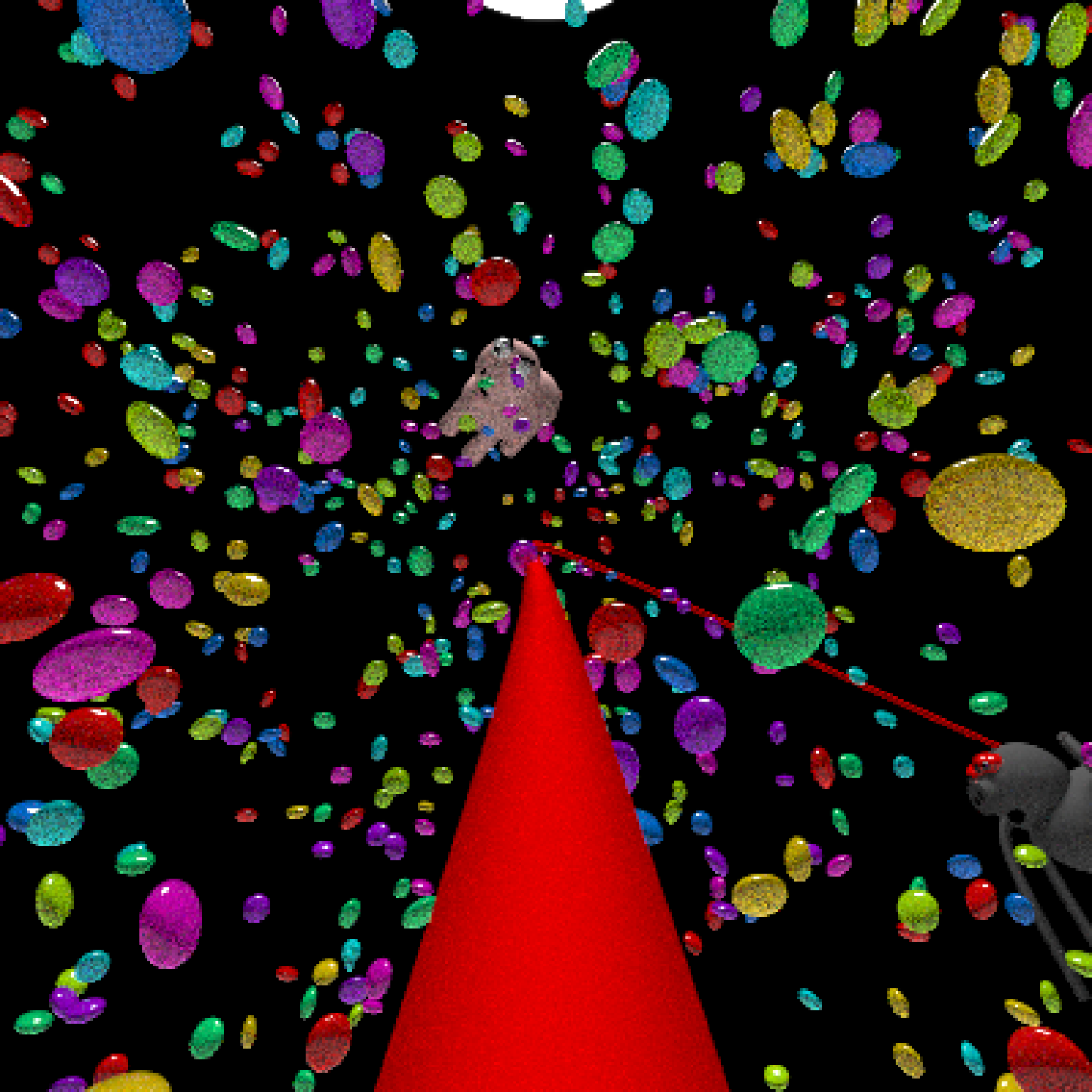
#Generate Camera movement, setting the lookat position to be same as camera position, but offset
#slightly in front. We'll render 12 frames, but you'd likely want more in a real animation.
camera_motion = generate_camera_motion(positions = camera_pos, lookats = camera_pos,
offset_lookat = 1, fovs=80, frames=12,
type="bezier")
#This returns a data frame of individual camera positions, interpolated by cubic bezier curves.
camera_motion
#Pass NA filename to plot to the device. We'll keep the path and offset it slightly to see
#where we're going. This results in a "roller coaster" effect.
generate_ground(material=diffuse(checkercolor="grey20"),depth=-10) %>%
add_object(ellip_scene) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=50,radius=10,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
add_object(obj_model(r_obj(simple_r = TRUE),x=10,y=-10,scale_obj=3, angle=c(0,-45,0),
material=dielectric(attenuation=c(1,1,0.3)))) %>%
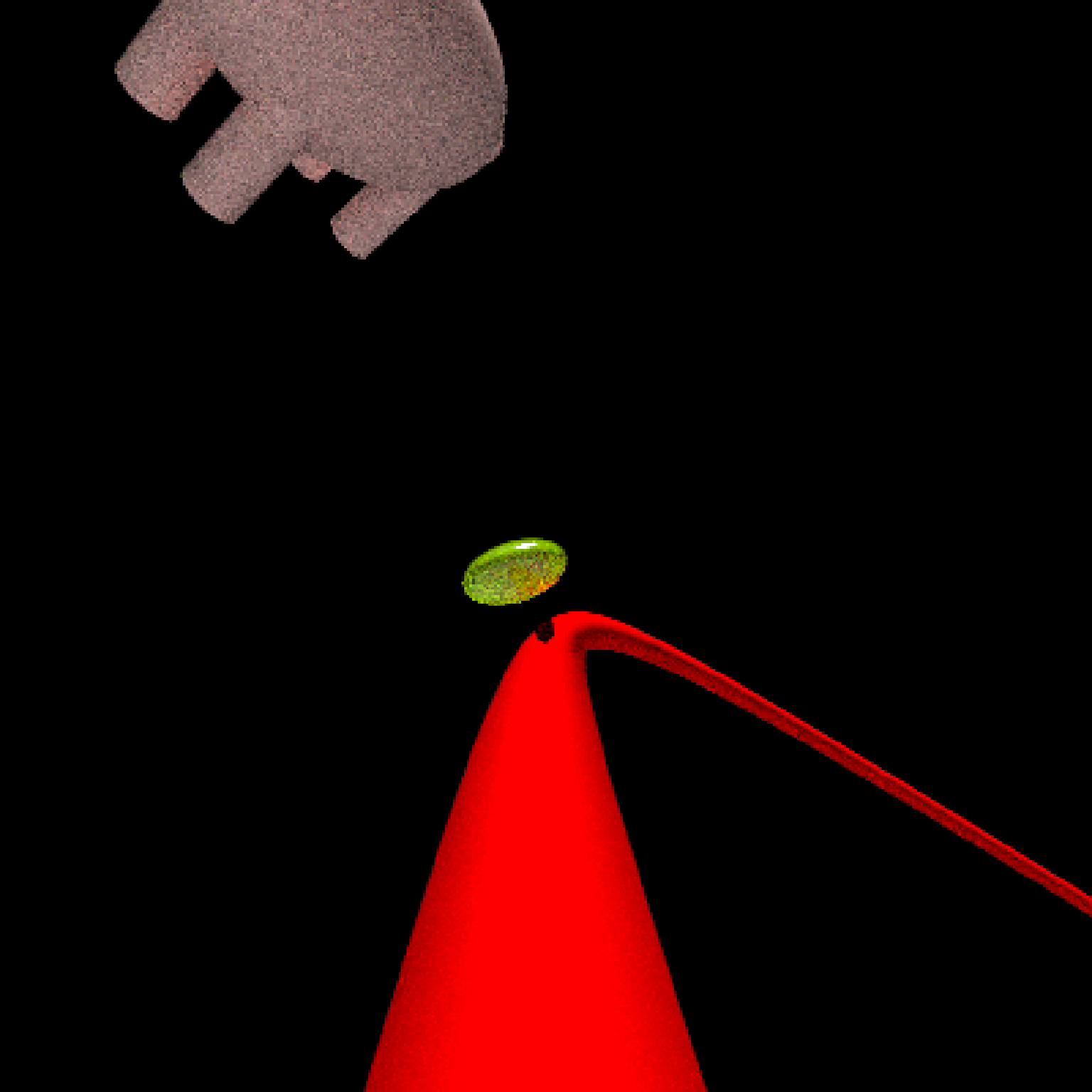
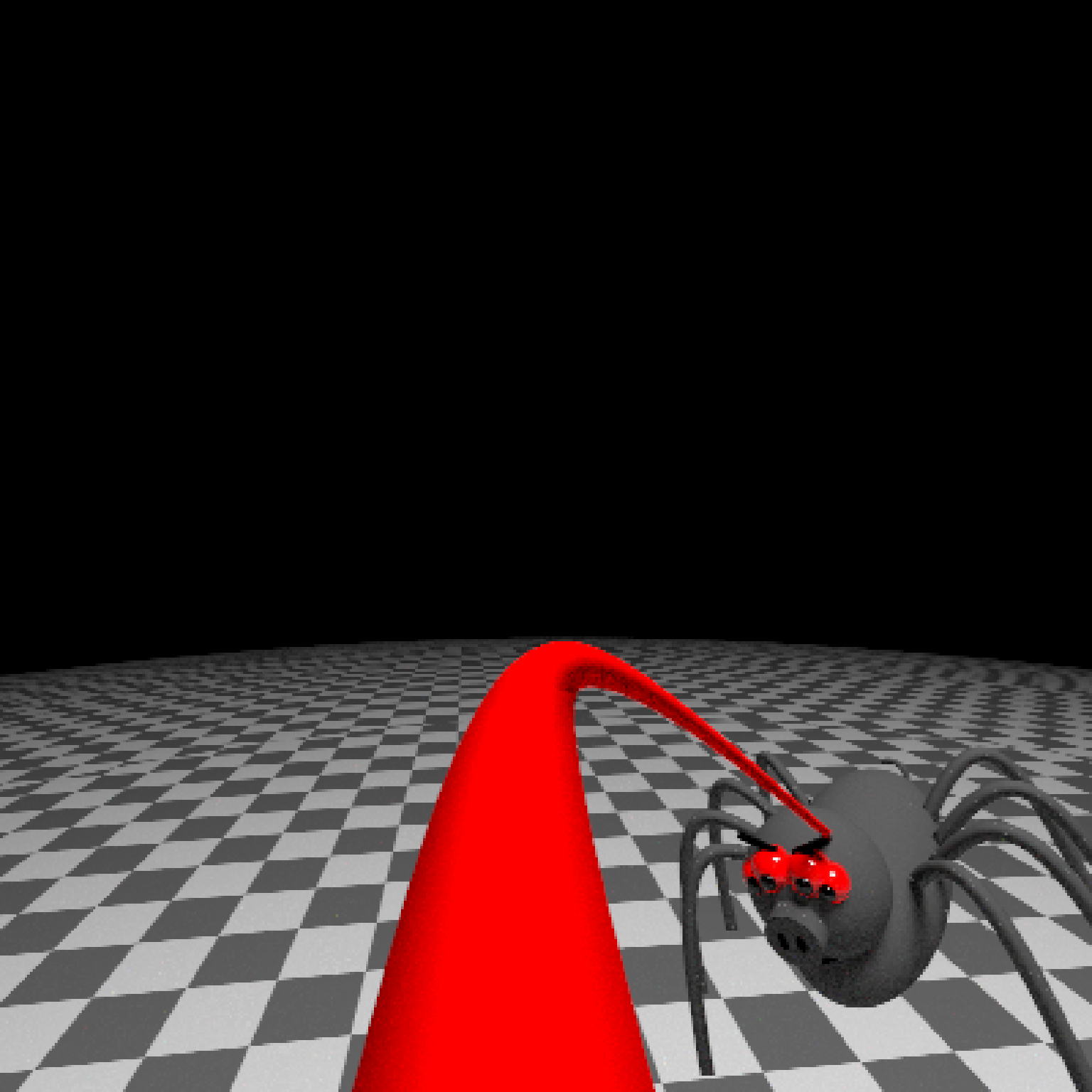
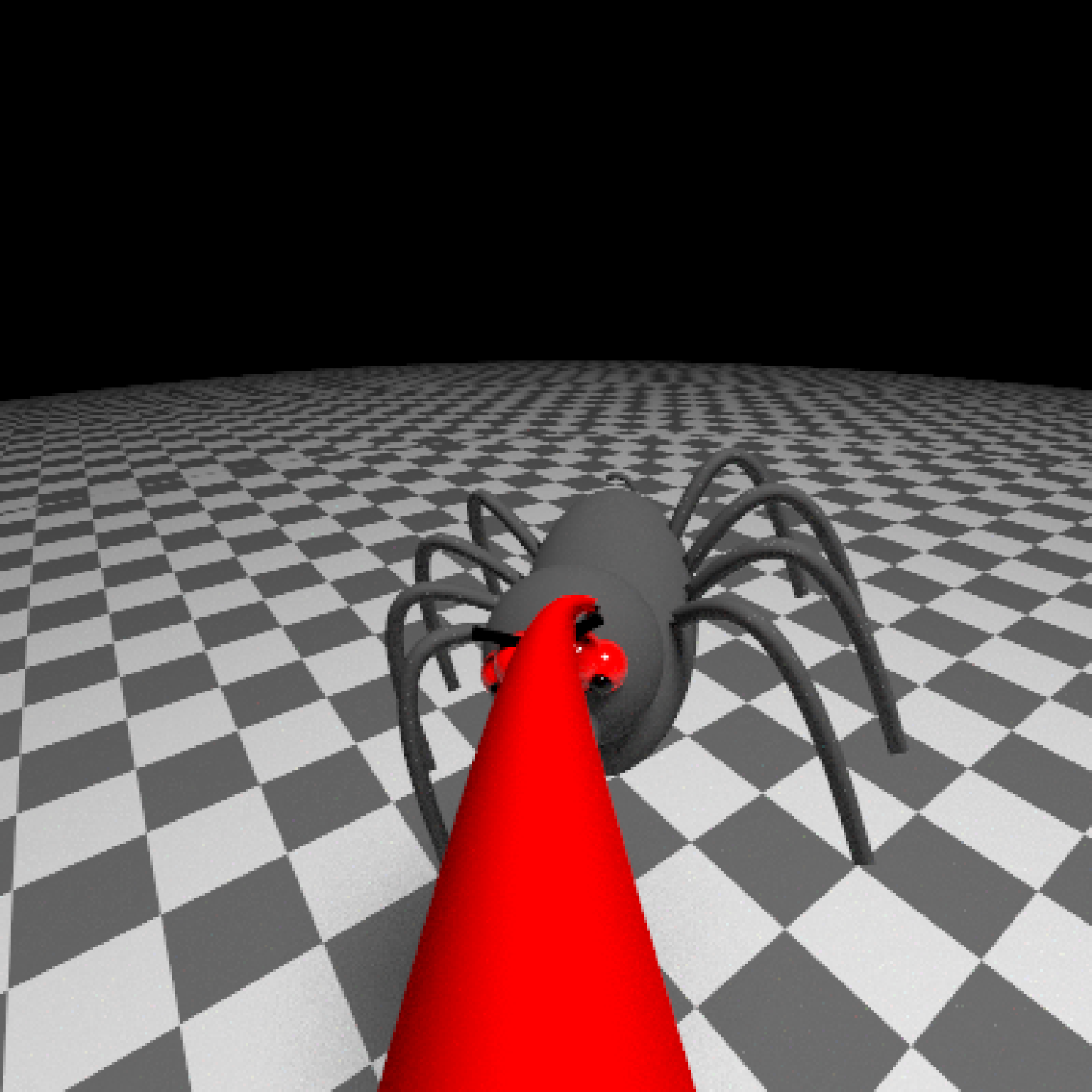
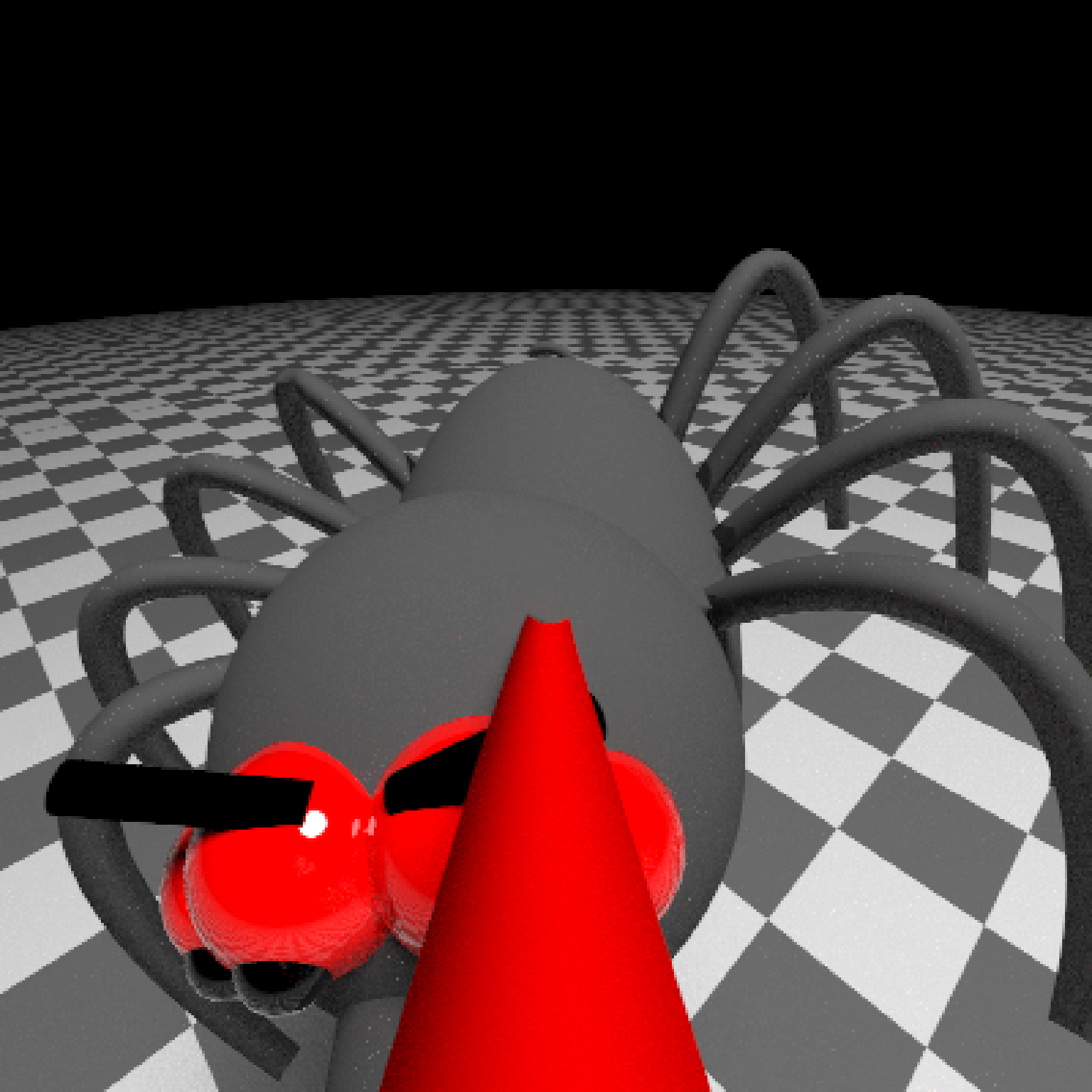
add_object(pig(x=-7,y=10,z=-5,scale=1,angle=c(0,-45,80),emotion="angry")) %>%
add_object(pig(x=0,y=-0.25,z=-15,scale=1,angle=c(0,225,-22), order_rotation = c(3,2,1),
emotion="angry", spider=TRUE)) %>%
add_object(path(camera_pos, y=-0.2,material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
render_animation(filename = NA, camera_motion = camera_motion, samples=16,
sample_method="sobol_blue",
clamp_value=10, width=400, height=400)
}
if(run_documentation()) {
#Generate Camera movement, setting the lookat position to be same as camera position, but offset
#slightly in front. We'll render 12 frames, but you'd likely want more in a real animation.
camera_motion = generate_camera_motion(positions = camera_pos, lookats = camera_pos,
offset_lookat = 1, fovs=80, frames=12,
type="bezier")
#This returns a data frame of individual camera positions, interpolated by cubic bezier curves.
camera_motion
#Pass NA filename to plot to the device. We'll keep the path and offset it slightly to see
#where we're going. This results in a "roller coaster" effect.
generate_ground(material=diffuse(checkercolor="grey20"),depth=-10) %>%
add_object(ellip_scene) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=50,radius=10,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
add_object(obj_model(r_obj(simple_r = TRUE),x=10,y=-10,scale_obj=3, angle=c(0,-45,0),
material=dielectric(attenuation=c(1,1,0.3)))) %>%
add_object(pig(x=-7,y=10,z=-5,scale=1,angle=c(0,-45,80),emotion="angry")) %>%
add_object(pig(x=0,y=-0.25,z=-15,scale=1,angle=c(0,225,-22), order_rotation = c(3,2,1),
emotion="angry", spider=TRUE)) %>%
add_object(path(camera_pos, y=-0.2,material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
render_animation(filename = NA, camera_motion = camera_motion, samples=16,
sample_method="sobol_blue",
clamp_value=10, width=400, height=400)
}