Takes the scene description and renders an image, either to the device or to a filename.
render_animation(
scene,
camera_motion,
start_frame = 1,
end_frame = NA,
width = 400,
height = 400,
preview = interactive(),
denoise = TRUE,
camera_description_file = NA,
camera_scale = 1,
iso = 100,
film_size = 22,
samples = 100,
min_variance = 0,
min_adaptive_size = 8,
sample_method = "sobol",
ambient_occlusion = FALSE,
keep_colors = FALSE,
sample_dist = 10,
max_depth = 50,
roulette_active_depth = 10,
ambient_light = FALSE,
clamp_value = Inf,
filename = NA,
backgroundhigh = "#80b4ff",
backgroundlow = "#ffffff",
shutteropen = 0,
shutterclose = 1,
focal_distance = NULL,
ortho_dimensions = c(1, 1),
tonemap = "raw",
bloom = TRUE,
parallel = TRUE,
bvh_type = "sah",
environment_light = NULL,
rotate_env = 0,
intensity_env = 1,
debug_channel = "none",
plot_scene = TRUE,
progress = interactive(),
verbose = FALSE,
transparent_background = FALSE,
preview_light_direction = c(0, -1, 0),
preview_exponent = 6,
integrator_type = "rtiow"
)Arguments
- scene
Tibble of object locations and properties.
- camera_motion
Data frame of camera motion vectors, calculated with `generate_camera_motion()`.
- start_frame
Default `1`. Frame to start the animation.
- end_frame
Default `NA`. By default, this is set to `nrow(camera_motion)`, the full number of frames.
- width
Default `400`. Width of the render, in pixels.
- height
Default `400`. Height of the render, in pixels.
- preview
Default `interactive()`. Whether to display a realtime progressive preview of the render. Press ESC to cancel the render.
- denoise
Default `TRUE`. Whether to de-noise the final image and preview images. Note, this requires the free Intel Open Image Denoise (OIDN) library be installed on your system. Pre-compiled binaries can be installed from ppenimagedenoise.org, as well as . Linking during rayrender installation is done by defining the environment variable OIDN_PATH (set it in the .Renviron file by calling `usethis::edit_r_environ()`) to the top-level directory for OIDN (the directory containing the "lib", "bin", and "include" directories) and re-installing this package from source.
- camera_description_file
Default `NA`. Filename of a camera description file for rendering with a realistic camera. Several camera files are built-in: `"50mm"`,`"wide"`,`"fisheye"`, and `"telephoto"`.
- camera_scale
Default `1`. Amount to scale the camera up or down in size. Use this rather than scaling a scene.
- iso
Default `100`. Camera exposure.
- film_size
Default `22`, in `mm` (scene units in `m`. Size of the film if using a realistic camera, otherwise ignored.
- samples
Default `100`. The maximum number of samples for each pixel. If this is a length-2 vector and the `sample_method` is `stratified`, this will control the number of strata in each dimension. The total number of samples in this case will be the product of the two numbers.
- min_variance
Default `0`. Minimum acceptable variance for a block of pixels for the adaptive sampler. Smaller numbers give higher quality images, at the expense of longer rendering times. If this is set to zero, the adaptive sampler will be turned off and the renderer will use the maximum number of samples everywhere.
- min_adaptive_size
Default `8`. Width of the minimum block size in the adaptive sampler.
- sample_method
Default `sobol`. The type of sampling method used to generate random numbers. The other options are `random` (worst quality but simple), `stratified` (only implemented for completion), and `sobol_blue` (best option for sample counts below 256).
- ambient_occlusion
Default `FALSE`. If `TRUE`, the animation will be rendered with the ambient occlusion renderer. This uses the background color specified in `backgroundhigh`
- keep_colors
Default `FALSE`. Whether to keep the diffuse material colors.
- sample_dist
Default `10`. Sample distance if `debug_channel = "ao"`.
- max_depth
Default `50`. Maximum number of bounces a ray can make in a scene.
- roulette_active_depth
Default `10`. Number of ray bounces until a ray can stop bouncing via Russian roulette.
- ambient_light
Default `FALSE`, unless there are no emitting objects in the scene. If `TRUE`, the background will be a gradient varying from `backgroundhigh` directly up (+y) to `backgroundlow` directly down (-y).
- clamp_value
Default `Inf`. If a bright light or a reflective material is in the scene, occasionally there will be bright spots that will not go away even with a large number of samples. These can be removed (at the cost of slightly darkening the image) by setting this to a small number greater than 1.
- filename
Default `NULL`. If present, the renderer will write to the filename instead of the current device.
- backgroundhigh
Default `#ffffff`. The "high" color in the background gradient. Can be either a hexadecimal code, or a numeric rgb vector listing three intensities between `0` and `1`.
- backgroundlow
Default `#ffffff`. The "low" color in the background gradient. Can be either a hexadecimal code, or a numeric rgb vector listing three intensities between `0` and `1`.
- shutteropen
Default `0`. Time at which the shutter is open. Only affects moving objects.
- shutterclose
Default `1`. Time at which the shutter is open. Only affects moving objects.
- focal_distance
Default `NULL`, automatically set to the `lookfrom-lookat` distance unless otherwise specified.
- ortho_dimensions
Default `c(1,1)`. Width and height of the orthographic camera. Will only be used if `fov = 0`.
- tonemap
Default `raw`, no tonemapping. See `rayimage::render_tonemap()` for options.
- bloom
Default `TRUE`. Set to `FALSE` to get the raw, pathtraced image. Otherwise, this performs a convolution of the HDR image of the scene with a sharp, long-tailed exponential kernel, which does not visibly affect dimly pixels, but does result in emitters light slightly bleeding into adjacent pixels. This provides an antialiasing effect for lights, even when tonemapping the image. Pass in a matrix to specify the convolution kernel manually, or a positive number to control the intensity of the bloom (higher number = more bloom).
- parallel
Default `FALSE`. If `TRUE`, it will use all available cores to render the image (or the number specified in `options("cores")` if that option is not `NULL`).
- bvh_type
Default `"sah"`, "surface area heuristic". Method of building the bounding volume hierarchy structure used when rendering. Other option is "equal", which splits tree into groups of equal size.
- environment_light
Default `NULL`. An image to be used for the background for rays that escape the scene. Supports both HDR (`.hdr`) and low-dynamic range (`.png`, `.jpg`) images.
- rotate_env
Default `0`. The number of degrees to rotate the environment map around the scene.
- intensity_env
Default `1`. The amount to increase the intensity of the environment lighting. Useful if using a LDR (JPEG or PNG) image as an environment map.
- debug_channel
Default `none`. If `depth`, function will return a depth map of rays into the scene instead of an image. If `normals`, function will return an image of scene normals, mapped from 0 to 1. If `uv`, function will return an image of the uv coords. If `variance`, function will return an image showing the number of samples needed to take for each block to converge. If `dpdu` or `dpdv`, function will return an image showing the differential `u` and `u` coordinates. If `color`, function will return the raw albedo values (with white for `metal` and `dielectric` materials). If `preview`, an image rendered with `render_preview()` will be returned. Can set to `ao` to render an animation with the ambient occlusion renderer.
- plot_scene
Default `TRUE`. Whether to plot the rendered scene.
- progress
Default `TRUE` if interactive session, `FALSE` otherwise.
- verbose
Default `FALSE`. Prints information and timing information about scene construction and raytracing progress.
- transparent_background
Default `FALSE`. If `TRUE`, any initial camera rays that escape the scene will be marked as transparent in the final image. If for a pixel some rays escape and others hit a surface, those pixels will be partially transparent.
- preview_light_direction
Default `c(0,-1,0)`. Vector specifying the orientation for the global light using for phong shading.
- preview_exponent
Default `6`. Phong exponent.
- integrator_type
Default `"rtiow"` (the algorithm specified in the book "Raytracing in One Weekend", a basic form of path guiding). Other options include `"nee"` (Next Event Estimation, with direct light sampling) and `"basic"` (basic pathtracing, for high sample reference renders and debugging only).
Value
Raytraced plot to current device, or an image saved to a file.
Examples
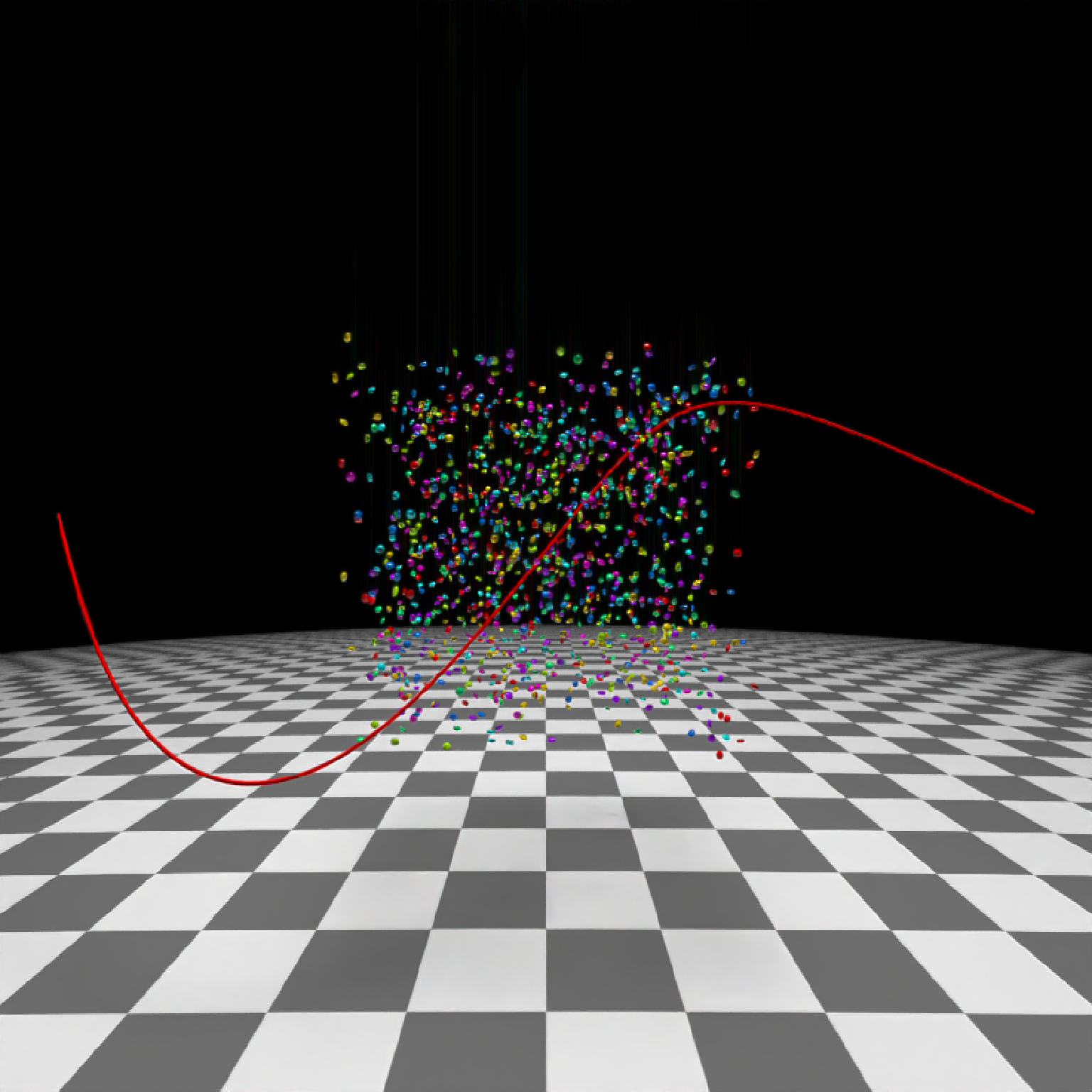
#Create and animate flying through a scene on a simulated roller coaster
if(run_documentation()) {
set.seed(3)
elliplist = list()
ellip_colors = rainbow(8)
for(i in 1:1200) {
elliplist[[i]] = ellipsoid(x=10*runif(1)-5,y=10*runif(1)-5,z=10*runif(1)-5,
angle = 360*runif(3), a=0.1,b=0.05,c=0.1,
material=glossy(color=sample(ellip_colors,1)))
}
ellip_scene = do.call(rbind, elliplist)
camera_pos = list(c(0,1,15),c(5,-5,5),c(-5,5,-5),c(0,1,-15))
#Plot the camera path and render from above using the path object:
generate_ground(material=diffuse(checkercolor="grey20"),depth=-10) %>%
add_object(ellip_scene) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=50,radius=10,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
add_object(path(camera_pos, material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
render_scene(lookfrom=c(0,20,0), width=800,height=800,samples=32,
camera_up = c(0,0,1),
fov=80)
}
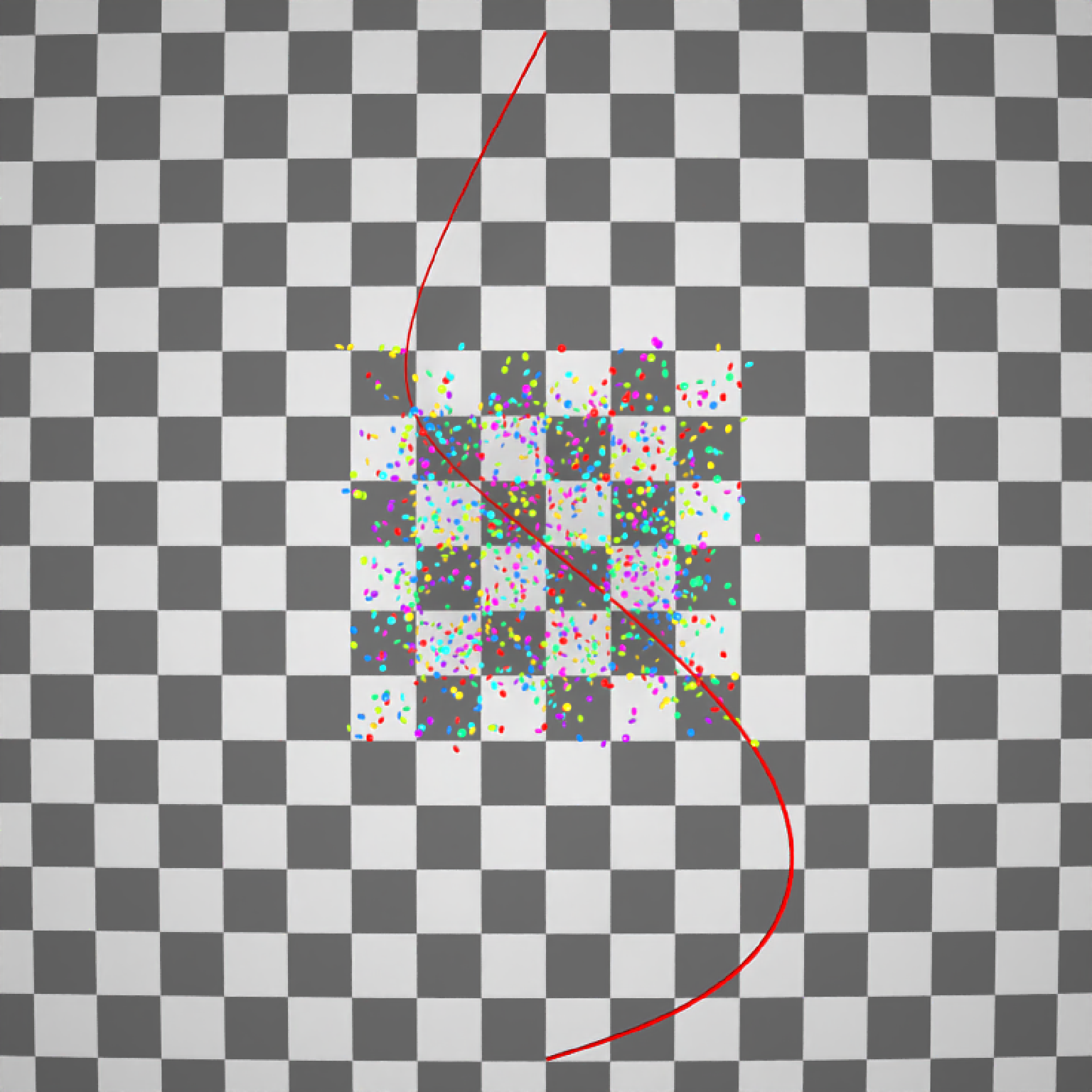 if(run_documentation()) {
#Side view
generate_ground(material=diffuse(checkercolor="grey20"),depth=-10) %>%
add_object(ellip_scene) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=50,radius=10,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
add_object(path(camera_pos, material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
render_scene(lookfrom=c(20,0,0),width=800,height=800,samples=32,
fov=80)
}
if(run_documentation()) {
#Side view
generate_ground(material=diffuse(checkercolor="grey20"),depth=-10) %>%
add_object(ellip_scene) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=50,radius=10,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
add_object(path(camera_pos, material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
render_scene(lookfrom=c(20,0,0),width=800,height=800,samples=32,
fov=80)
}
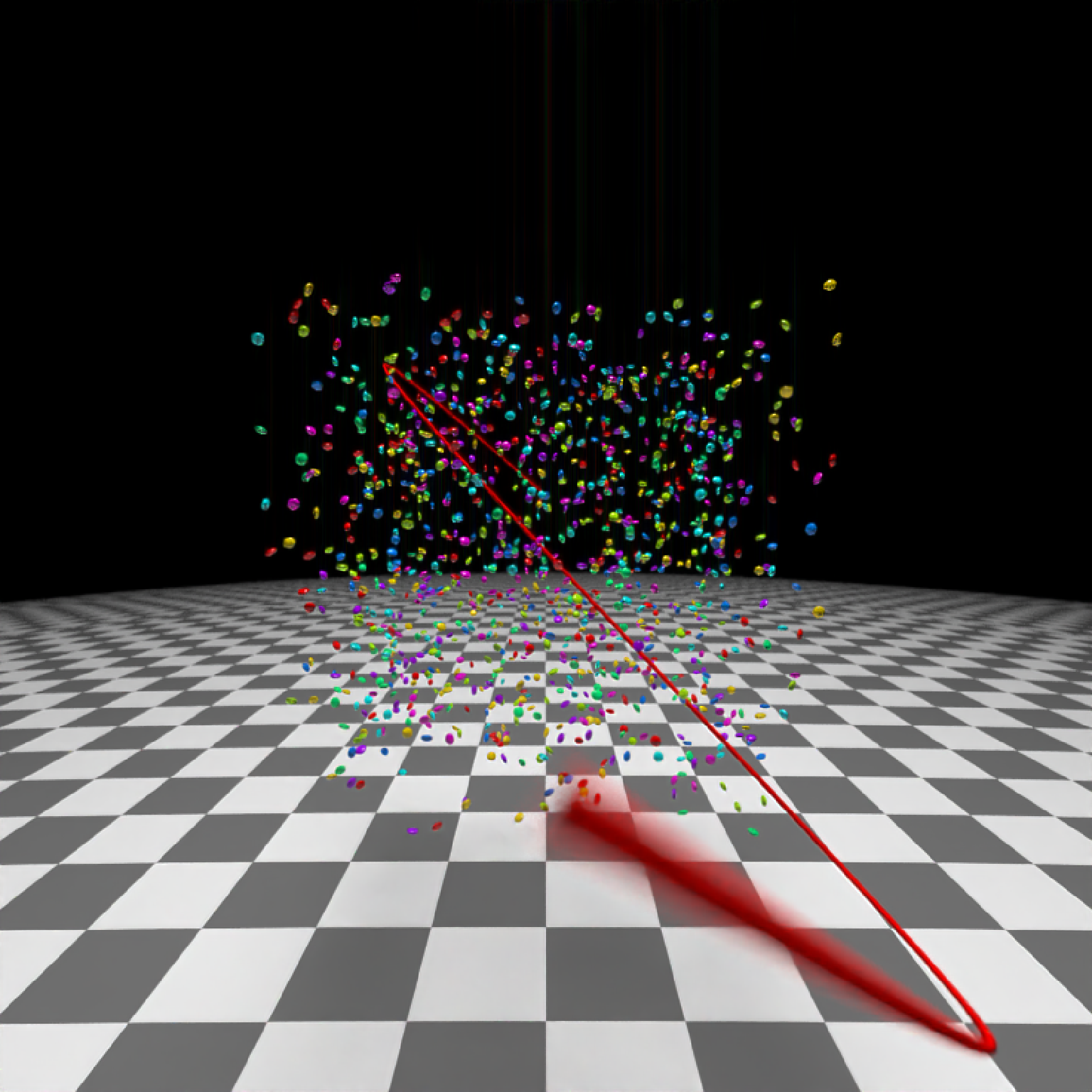
 if(run_documentation()) {
#View from the start
generate_ground(material=diffuse(checkercolor="grey20"),depth=-10) %>%
add_object(ellip_scene) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=50,radius=10,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
add_object(path(camera_pos, material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
render_scene(lookfrom=c(0,1.5,16),width=800,height=800,samples=32,
fov=80)
}
if(run_documentation()) {
#View from the start
generate_ground(material=diffuse(checkercolor="grey20"),depth=-10) %>%
add_object(ellip_scene) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=50,radius=10,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
add_object(path(camera_pos, material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
render_scene(lookfrom=c(0,1.5,16),width=800,height=800,samples=32,
fov=80)
}
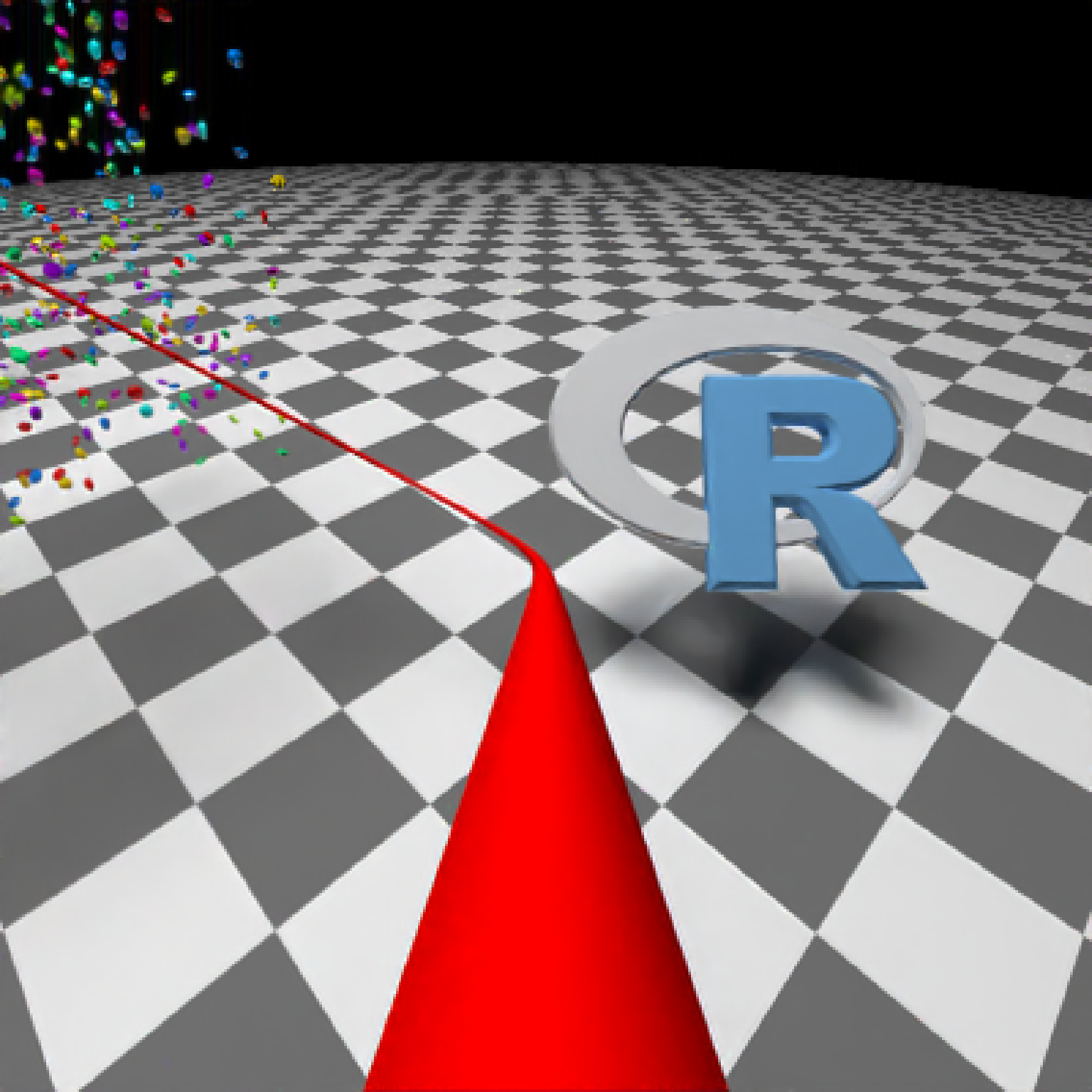
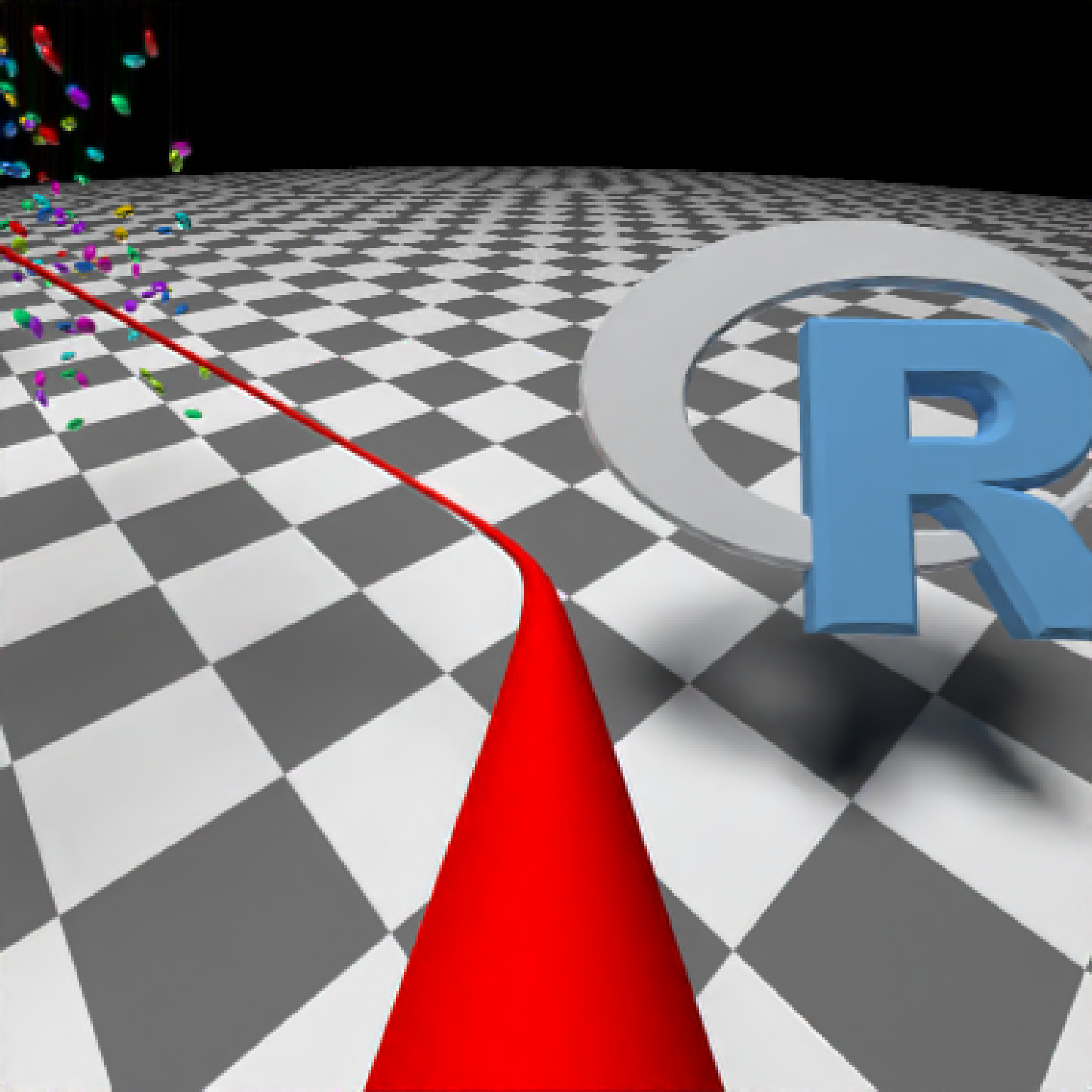
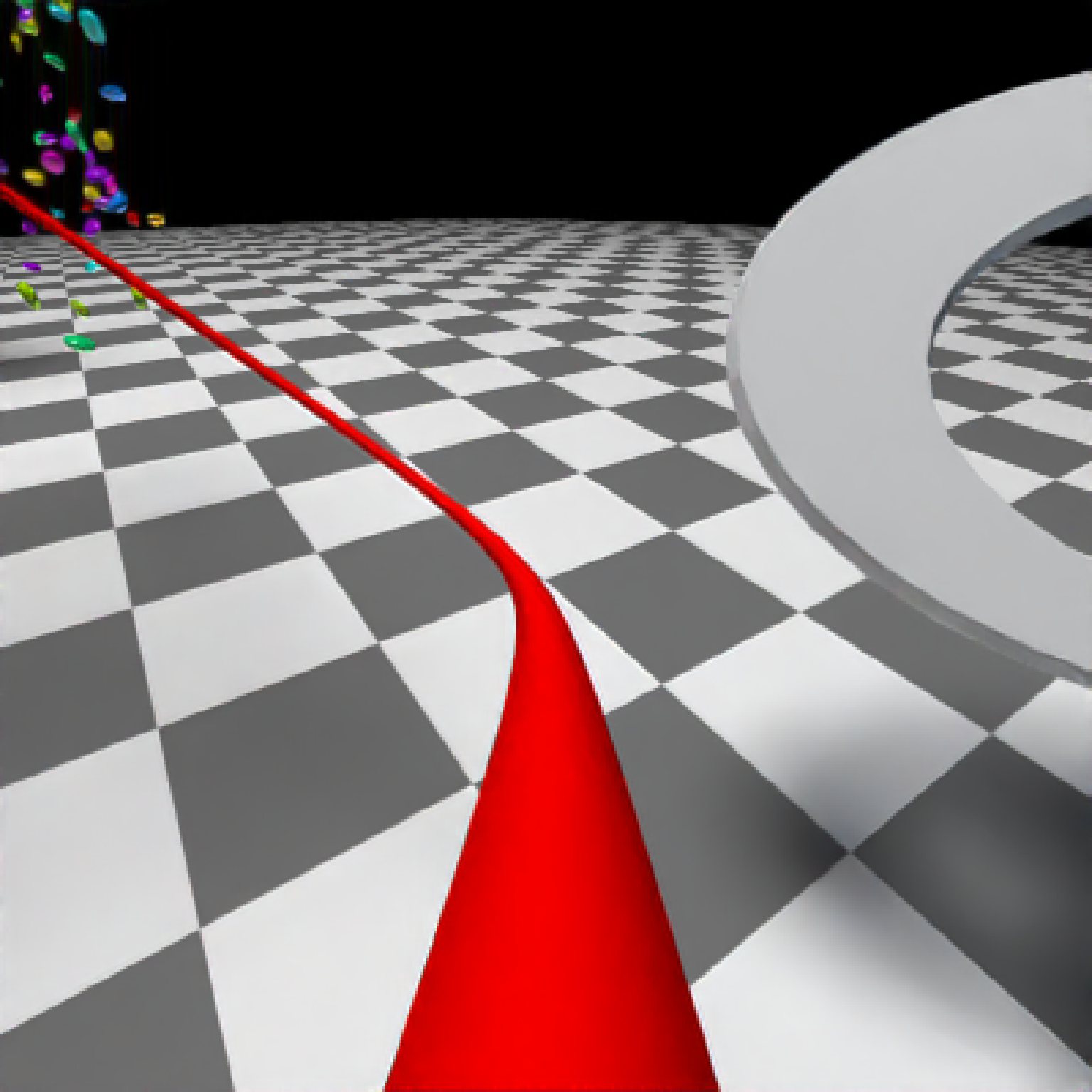
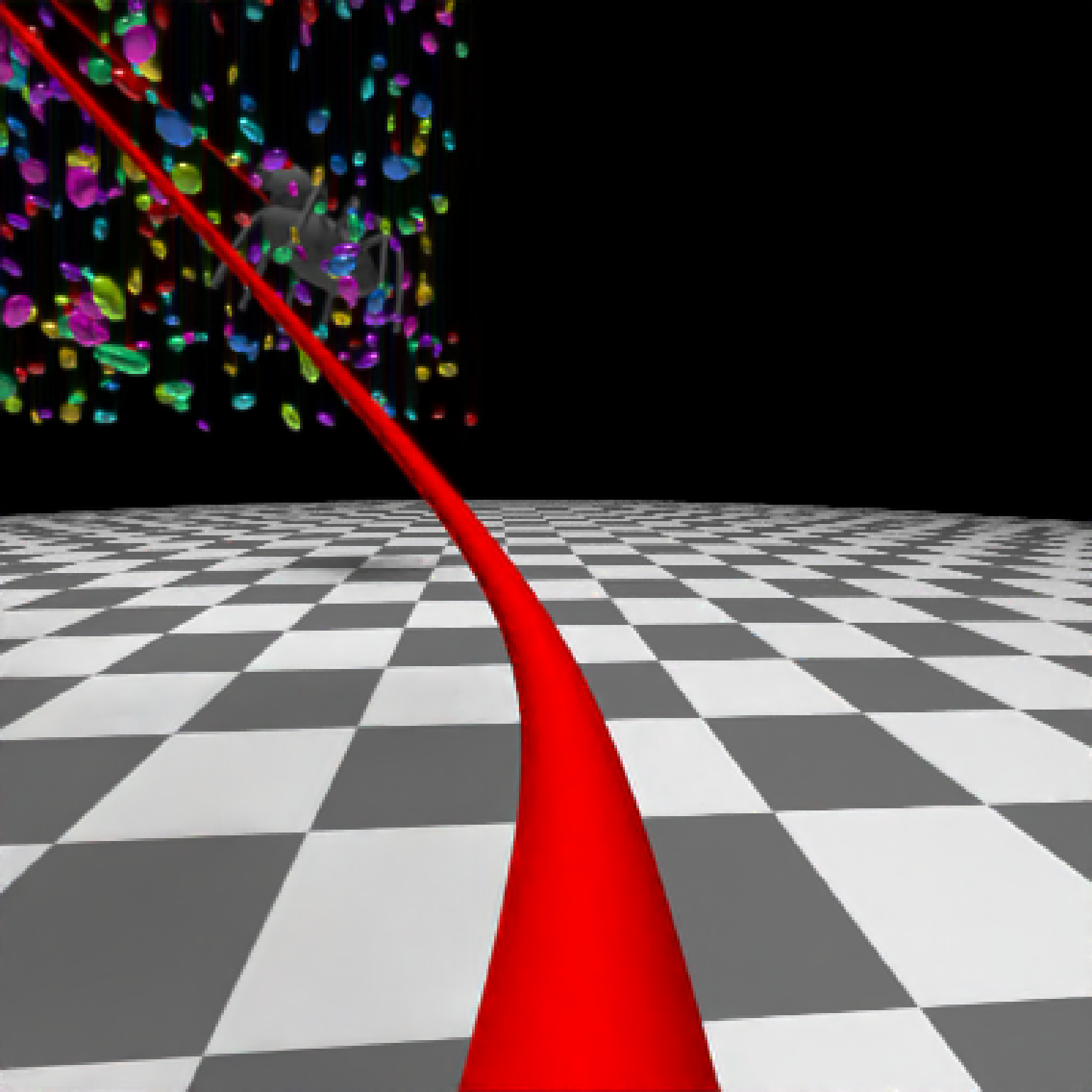
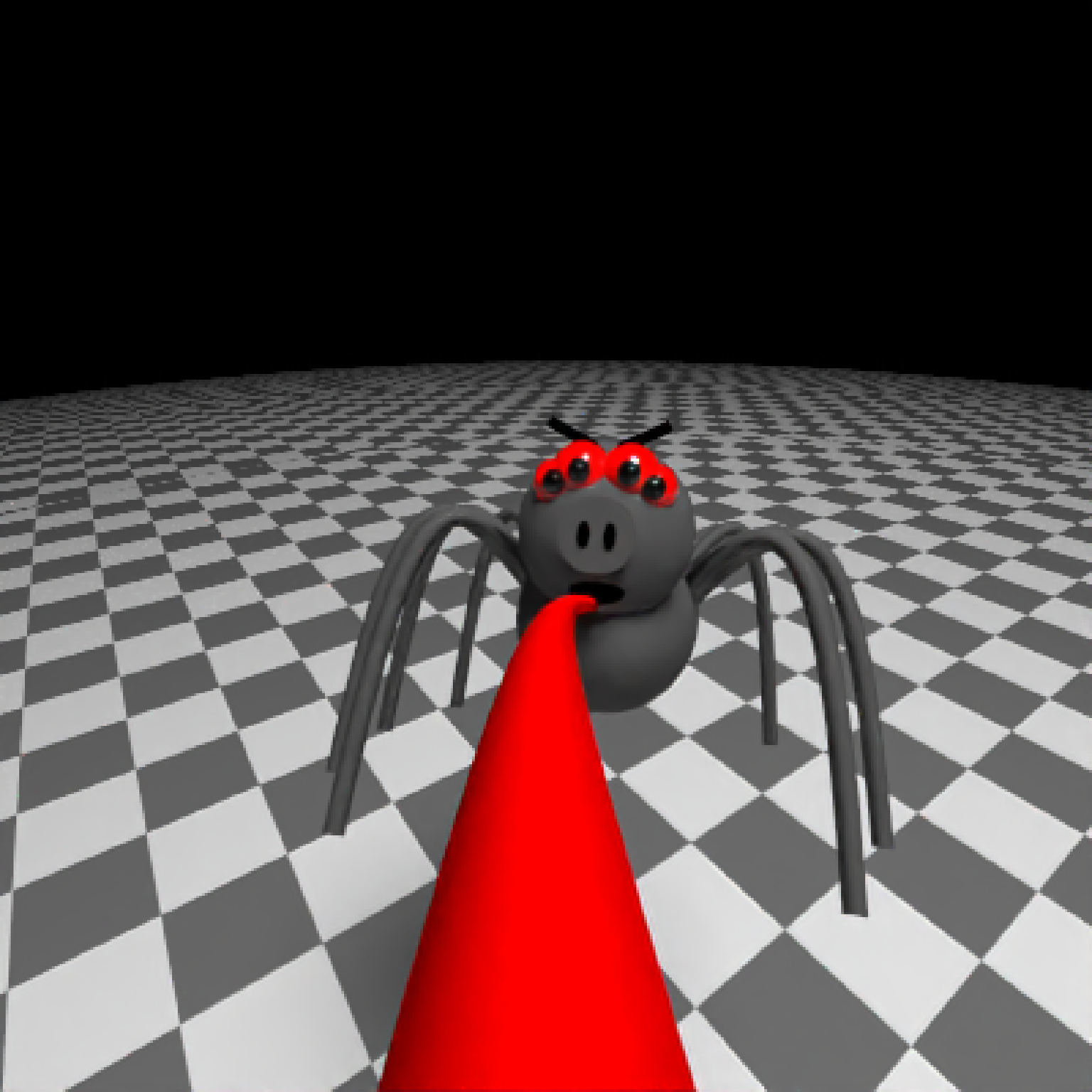
 if(run_documentation()) {
#Generate Camera movement, setting the lookat position to be same as camera position, but offset
#slightly in front. We'll render 12 frames, but you'd likely want more in a real animation.
camera_motion = generate_camera_motion(positions = camera_pos, lookats = camera_pos,
offset_lookat = 1, fovs=80, frames=12,
type="bezier")
#This returns a data frame of individual camera positions, interpolated by cubic bezier curves.
camera_motion
#Pass NA filename to plot to the device. We'll keep the path and offset it slightly to see
#where we're going. This results in a "roller coaster" effect.
generate_ground(material=diffuse(checkercolor="grey20"),depth=-10) %>%
add_object(ellip_scene) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=50,radius=10,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
add_object(obj_model(r_obj(),x=10,y=-5,z=10,scale=7, angle=c(-45,-45,0),
material=dielectric(attenuation=c(1,1,0.3)))) %>%
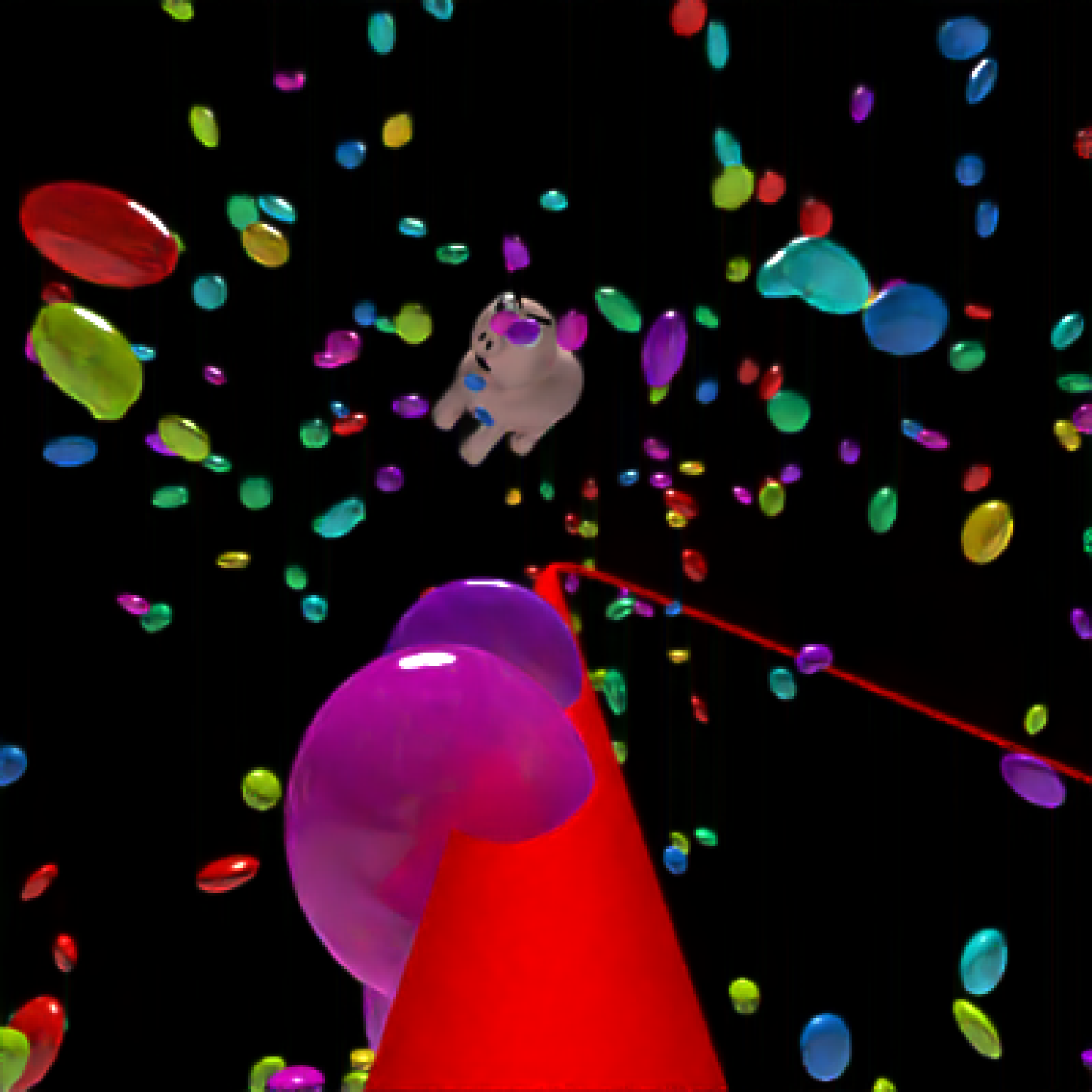
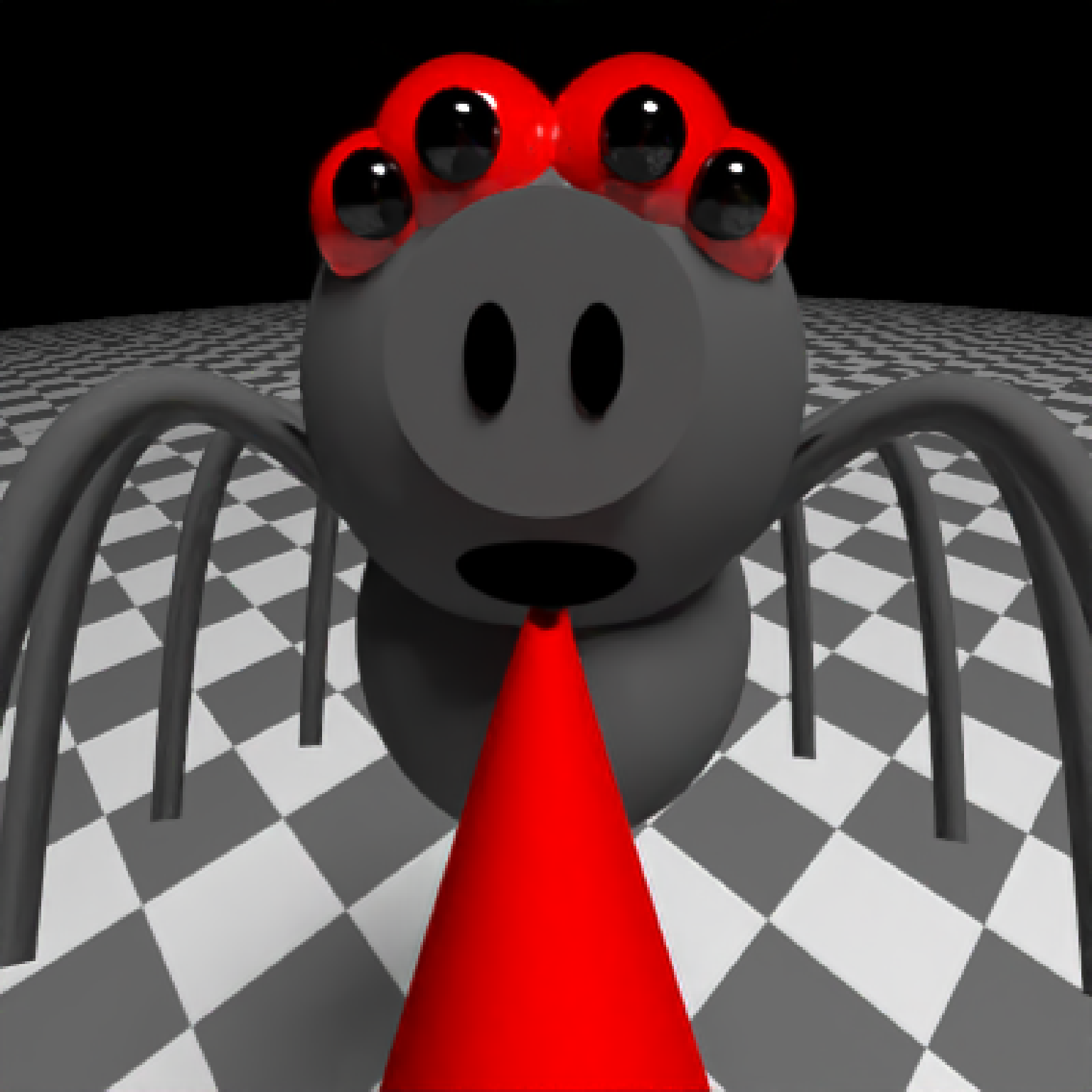
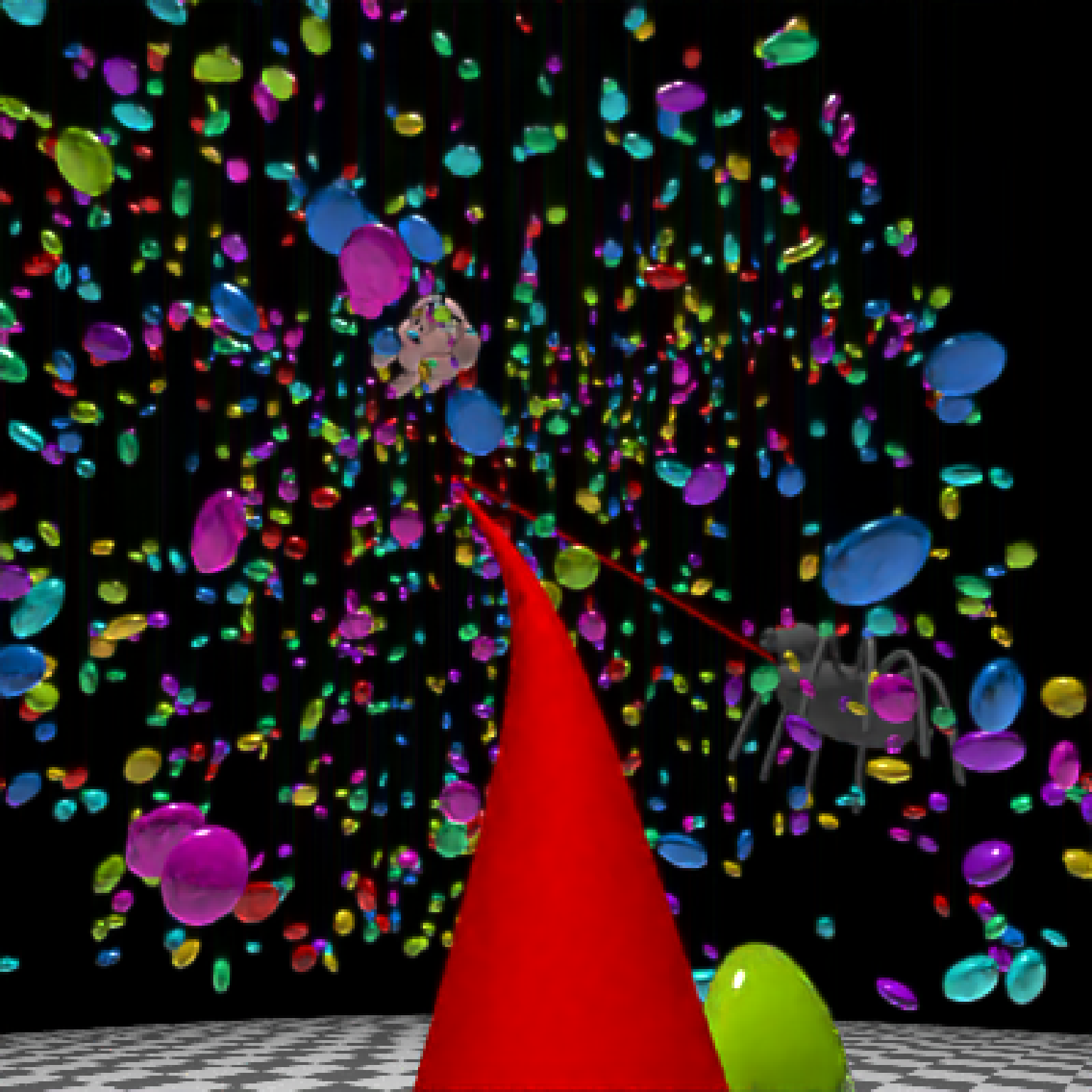
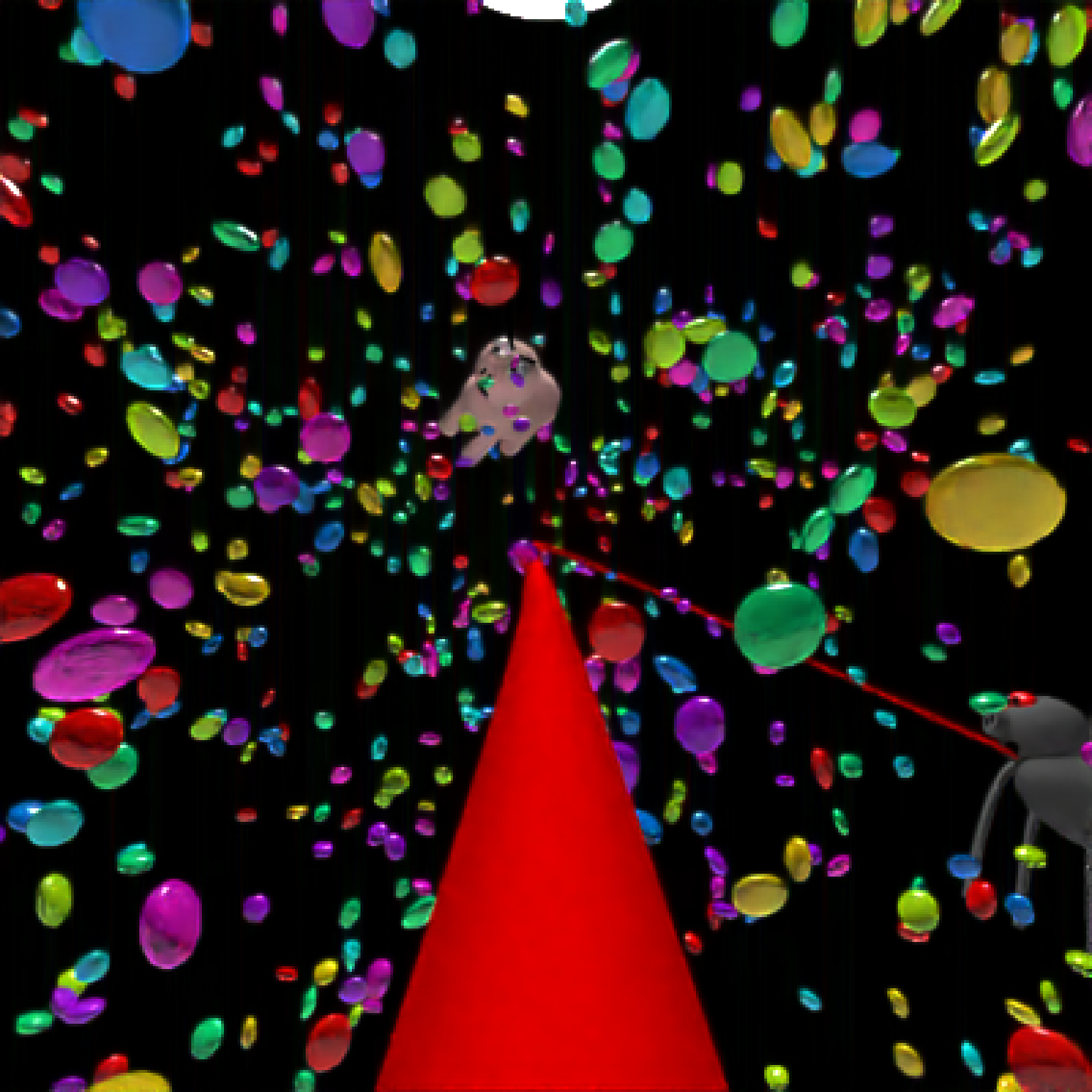
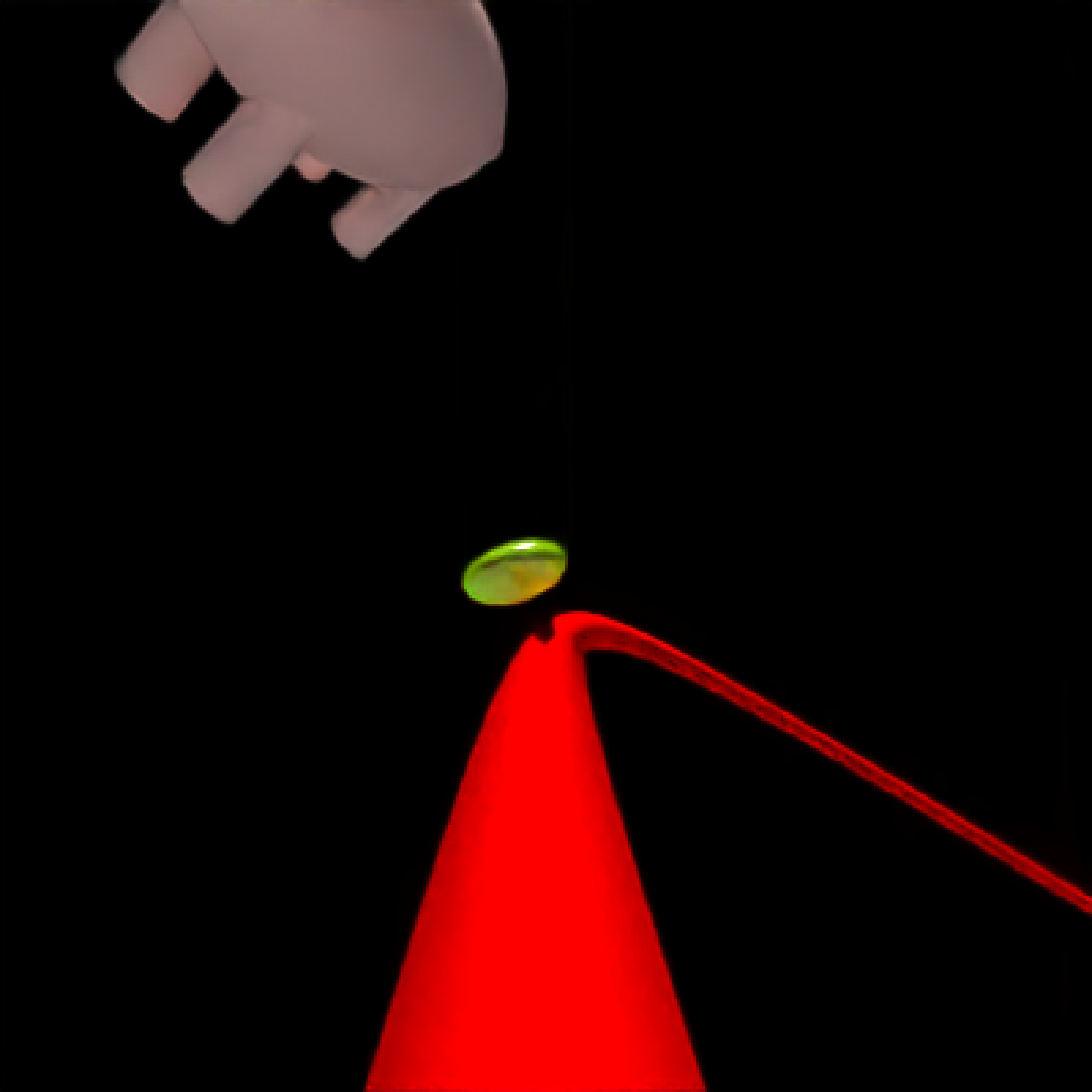
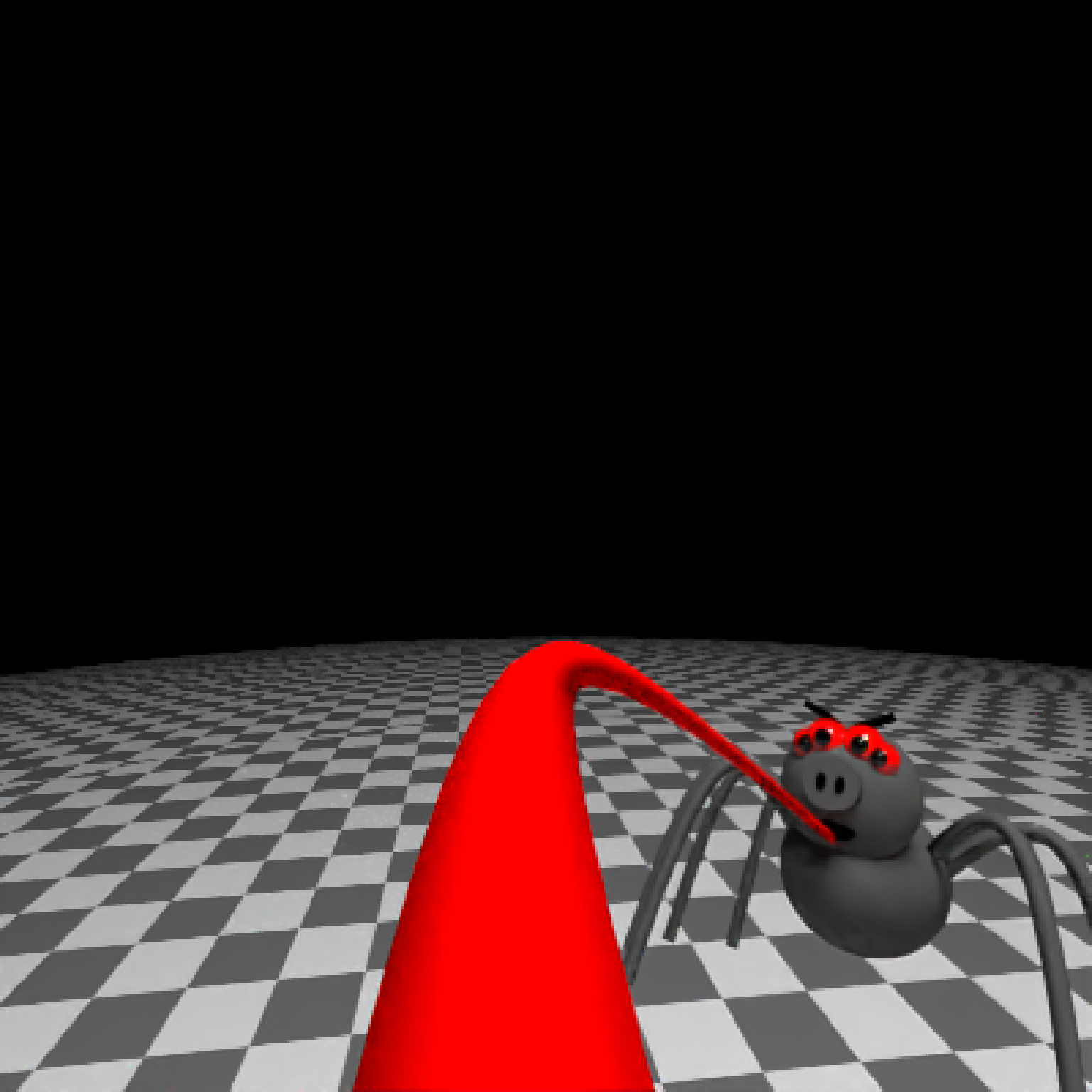
add_object(pig(x=-7,y=10,z=-5,scale=1,angle=c(0,-45,80),emotion="angry")) %>%
add_object(pig(x=0,y=-0.25,z=-15,scale=1,angle=c(0,225,-22), order_rotation = c(3,2,1),
emotion="angry", spider=TRUE)) %>%
add_object(path(camera_pos, y=-0.2,material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
render_animation(filename = NA, camera_motion = camera_motion, samples=16,
sample_method="sobol_blue",
clamp_value=10, width=400, height=400)
}
if(run_documentation()) {
#Generate Camera movement, setting the lookat position to be same as camera position, but offset
#slightly in front. We'll render 12 frames, but you'd likely want more in a real animation.
camera_motion = generate_camera_motion(positions = camera_pos, lookats = camera_pos,
offset_lookat = 1, fovs=80, frames=12,
type="bezier")
#This returns a data frame of individual camera positions, interpolated by cubic bezier curves.
camera_motion
#Pass NA filename to plot to the device. We'll keep the path and offset it slightly to see
#where we're going. This results in a "roller coaster" effect.
generate_ground(material=diffuse(checkercolor="grey20"),depth=-10) %>%
add_object(ellip_scene) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=50,radius=10,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
add_object(obj_model(r_obj(),x=10,y=-5,z=10,scale=7, angle=c(-45,-45,0),
material=dielectric(attenuation=c(1,1,0.3)))) %>%
add_object(pig(x=-7,y=10,z=-5,scale=1,angle=c(0,-45,80),emotion="angry")) %>%
add_object(pig(x=0,y=-0.25,z=-15,scale=1,angle=c(0,225,-22), order_rotation = c(3,2,1),
emotion="angry", spider=TRUE)) %>%
add_object(path(camera_pos, y=-0.2,material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
render_animation(filename = NA, camera_motion = camera_motion, samples=16,
sample_method="sobol_blue",
clamp_value=10, width=400, height=400)
}