Extruded Polygon Object
extruded_polygon(
polygon = NULL,
x = 0,
y = 0,
z = 0,
plane = "xz",
top = 1,
bottom = 0,
holes = NULL,
angle = c(0, 0, 0),
order_rotation = c(1, 2, 3),
material = diffuse(),
center = FALSE,
flip_horizontal = FALSE,
flip_vertical = FALSE,
data_column_top = NULL,
data_column_bottom = NULL,
scale_data = 1,
scale = c(1, 1, 1)
)Arguments
- polygon
`sf` object, "SpatialPolygon" `sp` object, or xy coordinates of polygon represented in a way that can be processed by `xy.coords()`. If xy-coordinate based polygons are open, they will be closed by adding an edge from the last point to the first. If the `sf` object contains MULTIPOLYGONZ data, it will flattened.
- x
Default `0`. x-coordinate to offset the extruded model.
- y
Default `0`. y-coordinate to offset the extruded model.
- z
Default `0`. z-coordinate to offset the extruded model.
- plane
Default `xz`. The plane the polygon is drawn in. All possibile orientations are `xz`, `zx`, `xy`, `yx`, `yz`, and `zy`.
- top
Default `1`. Extruded top distance. If this equals `bottom`, the polygon will not be extruded and just the one side will be rendered.
- bottom
Default `0`. Extruded bottom distance. If this equals `top`, the polygon will not be extruded and just the one side will be rendered.
- holes
Default `0`. If passing in a polygon directly, this specifies which index represents the holes in the polygon. See the `earcut` function in the `decido` package for more information.
- angle
Default `c(0, 0, 0)`. Angle of rotation around the x, y, and z axes, applied in the order specified in `order_rotation`.
- order_rotation
Default `c(1, 2, 3)`. The order to apply the rotations, referring to "x", "y", and "z".
- material
Default
diffuse.The material, called from one of the material functionsdiffuse,metal, ordielectric.- center
Default `FALSE`. Whether to center the polygon at the origin.
- flip_horizontal
Default `FALSE`. Flip polygon horizontally in the plane defined by `plane`.
- flip_vertical
Default `FALSE`. Flip polygon vertically in the plane defined by `plane`.
- data_column_top
Default `NULL`. A string indicating the column in the `sf` object to use to specify the top of the extruded polygon.
- data_column_bottom
Default `NULL`. A string indicating the column in the `sf` object to use to specify the bottom of the extruded polygon.
- scale_data
Default `1`. If specifying `data_column_top` or `data_column_bottom`, how much to scale that value when rendering.
- scale
Default `c(1, 1, 1)`. Scale transformation in the x, y, and z directions. If this is a single value, number, the object will be scaled uniformly. Note: emissive objects may not currently function correctly when scaled.
Value
Multiple row tibble describing the extruded polygon in the scene.
Examples
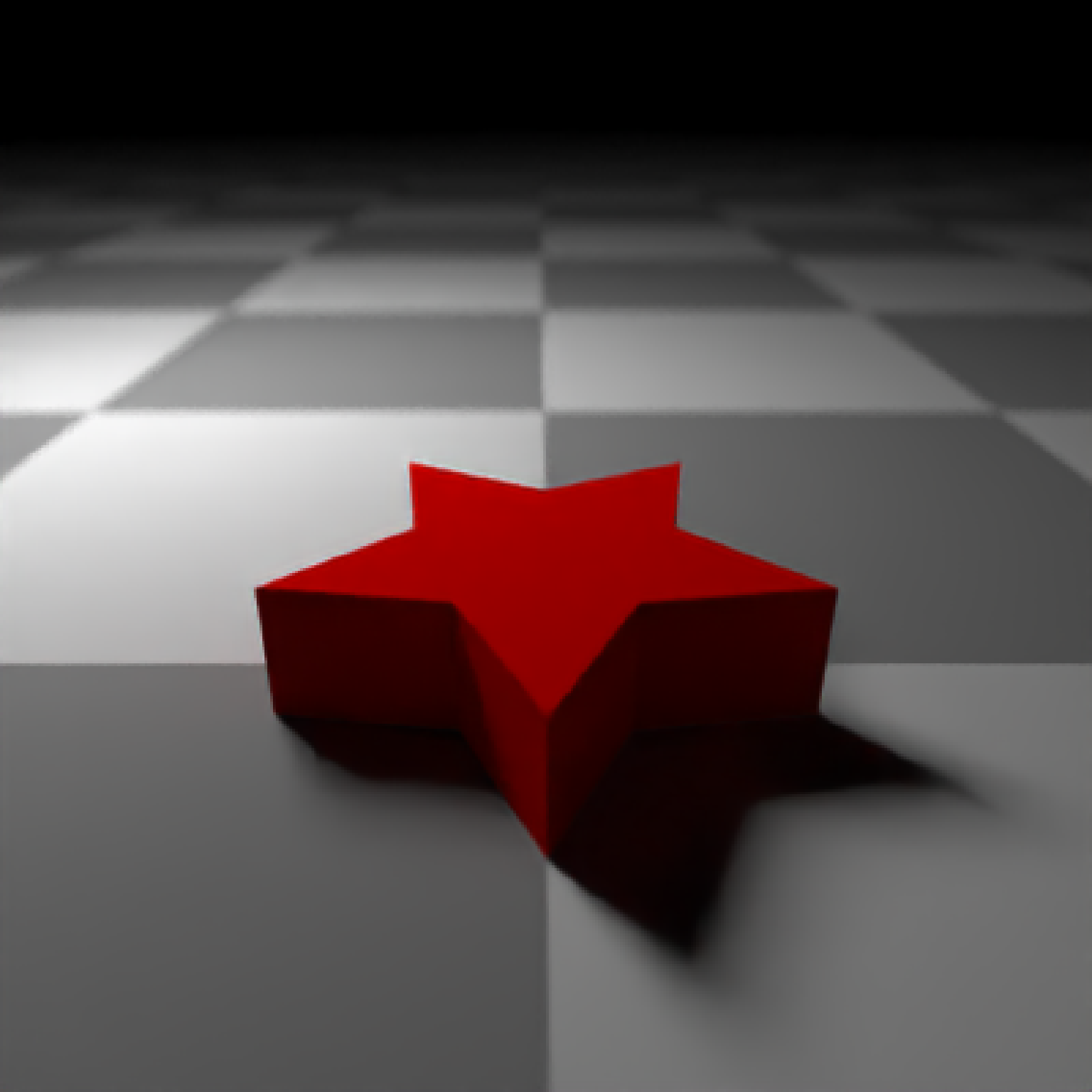
#Manually create a polygon object, here a star:
if(run_documentation()) {
angles = seq(0,360,by=36)
xx = rev(c(rep(c(1,0.5),5),1) * sinpi(angles/180))
yy = rev(c(rep(c(1,0.5),5),1) * cospi(angles/180))
star_polygon = data.frame(x=xx,y=yy)
}
if(run_documentation()) {
generate_ground(depth=0,
material = diffuse(color="grey50",checkercolor="grey20")) %>%
add_object(extruded_polygon(star_polygon,top=0.5,bottom=0,
material=diffuse(color="red",sigma=90))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=4,x=-3,z=-3,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
render_scene(parallel=TRUE,lookfrom = c(0,2,3),samples=16,lookat=c(0,0.5,0),fov=60)
}
 #Now, let's add a hole to the center of the polygon. We'll make the polygon
#hollow by shrinking it, combining it with the normal size polygon,
#and specify with the `holes` argument that everything after `nrow(star_polygon)`
#in the following should be used to draw a hole:
if(run_documentation()) {
hollow_star = rbind(star_polygon,0.8*star_polygon)
}
if(run_documentation()) {
generate_ground(depth=-0.01,
material = diffuse(color="grey50",checkercolor="grey20")) %>%
add_object(extruded_polygon(hollow_star,top=0.25,bottom=0, holes = nrow(star_polygon) + 1,
material=diffuse(color="red",sigma=90))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=4,x=-3,z=-3,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
render_scene(parallel=TRUE,lookfrom = c(0,2,4),samples=16,lookat=c(0,0,0),fov=30)
}
#> Warning: coercing argument of type 'double' to logical
#Now, let's add a hole to the center of the polygon. We'll make the polygon
#hollow by shrinking it, combining it with the normal size polygon,
#and specify with the `holes` argument that everything after `nrow(star_polygon)`
#in the following should be used to draw a hole:
if(run_documentation()) {
hollow_star = rbind(star_polygon,0.8*star_polygon)
}
if(run_documentation()) {
generate_ground(depth=-0.01,
material = diffuse(color="grey50",checkercolor="grey20")) %>%
add_object(extruded_polygon(hollow_star,top=0.25,bottom=0, holes = nrow(star_polygon) + 1,
material=diffuse(color="red",sigma=90))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=4,x=-3,z=-3,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
render_scene(parallel=TRUE,lookfrom = c(0,2,4),samples=16,lookat=c(0,0,0),fov=30)
}
#> Warning: coercing argument of type 'double' to logical
 # Render one in the y-x plane as well by changing the `plane` argument,
# as well as offset it slightly.
if(run_documentation()) {
generate_ground(depth=-0.01,
material = diffuse(color="grey50",checkercolor="grey20")) %>%
add_object(extruded_polygon(hollow_star,top=0.25,bottom=0, holes = nrow(star_polygon),
material=diffuse(color="red",sigma=90))) %>%
add_object(extruded_polygon(hollow_star,top=0.25,bottom=0, y=1.2, z=-1.2,
holes = nrow(star_polygon) + 1, plane = "yx",
material=diffuse(color="green",sigma=90))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=4,x=-3,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
render_scene(parallel=TRUE,lookfrom = c(0,2,4),samples=16,lookat=c(0,0.9,0),fov=40)
}
#> Warning: coercing argument of type 'double' to logical
# Render one in the y-x plane as well by changing the `plane` argument,
# as well as offset it slightly.
if(run_documentation()) {
generate_ground(depth=-0.01,
material = diffuse(color="grey50",checkercolor="grey20")) %>%
add_object(extruded_polygon(hollow_star,top=0.25,bottom=0, holes = nrow(star_polygon),
material=diffuse(color="red",sigma=90))) %>%
add_object(extruded_polygon(hollow_star,top=0.25,bottom=0, y=1.2, z=-1.2,
holes = nrow(star_polygon) + 1, plane = "yx",
material=diffuse(color="green",sigma=90))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=4,x=-3,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
render_scene(parallel=TRUE,lookfrom = c(0,2,4),samples=16,lookat=c(0,0.9,0),fov=40)
}
#> Warning: coercing argument of type 'double' to logical
 # Now add the zy plane:
if(run_documentation()) {
generate_ground(depth=-0.01,
material = diffuse(color="grey50",checkercolor="grey20")) %>%
add_object(extruded_polygon(hollow_star,top=0.25,bottom=0, holes = nrow(star_polygon) + 1,
material=diffuse(color="red",sigma=90))) %>%
add_object(extruded_polygon(hollow_star,top=0.25,bottom=0, y=1.2, z=-1.2,
holes = nrow(star_polygon) + 1, plane = "yx",
material=diffuse(color="green",sigma=90))) %>%
add_object(extruded_polygon(hollow_star,top=0.25,bottom=0, y=1.2, x=1.2,
holes = nrow(star_polygon) + 1, plane = "zy",
material=diffuse(color="blue",sigma=90))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=4,x=-3,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
render_scene(parallel=TRUE,lookfrom = c(-4,2,4),samples=16,lookat=c(0,0.9,0),fov=40)
}
#> Warning: coercing argument of type 'double' to logical
#> Warning: coercing argument of type 'double' to logical
#> Warning: coercing argument of type 'double' to logical
# Now add the zy plane:
if(run_documentation()) {
generate_ground(depth=-0.01,
material = diffuse(color="grey50",checkercolor="grey20")) %>%
add_object(extruded_polygon(hollow_star,top=0.25,bottom=0, holes = nrow(star_polygon) + 1,
material=diffuse(color="red",sigma=90))) %>%
add_object(extruded_polygon(hollow_star,top=0.25,bottom=0, y=1.2, z=-1.2,
holes = nrow(star_polygon) + 1, plane = "yx",
material=diffuse(color="green",sigma=90))) %>%
add_object(extruded_polygon(hollow_star,top=0.25,bottom=0, y=1.2, x=1.2,
holes = nrow(star_polygon) + 1, plane = "zy",
material=diffuse(color="blue",sigma=90))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=4,x=-3,material=light(intensity=30))) %>%
render_scene(parallel=TRUE,lookfrom = c(-4,2,4),samples=16,lookat=c(0,0.9,0),fov=40)
}
#> Warning: coercing argument of type 'double' to logical
#> Warning: coercing argument of type 'double' to logical
#> Warning: coercing argument of type 'double' to logical
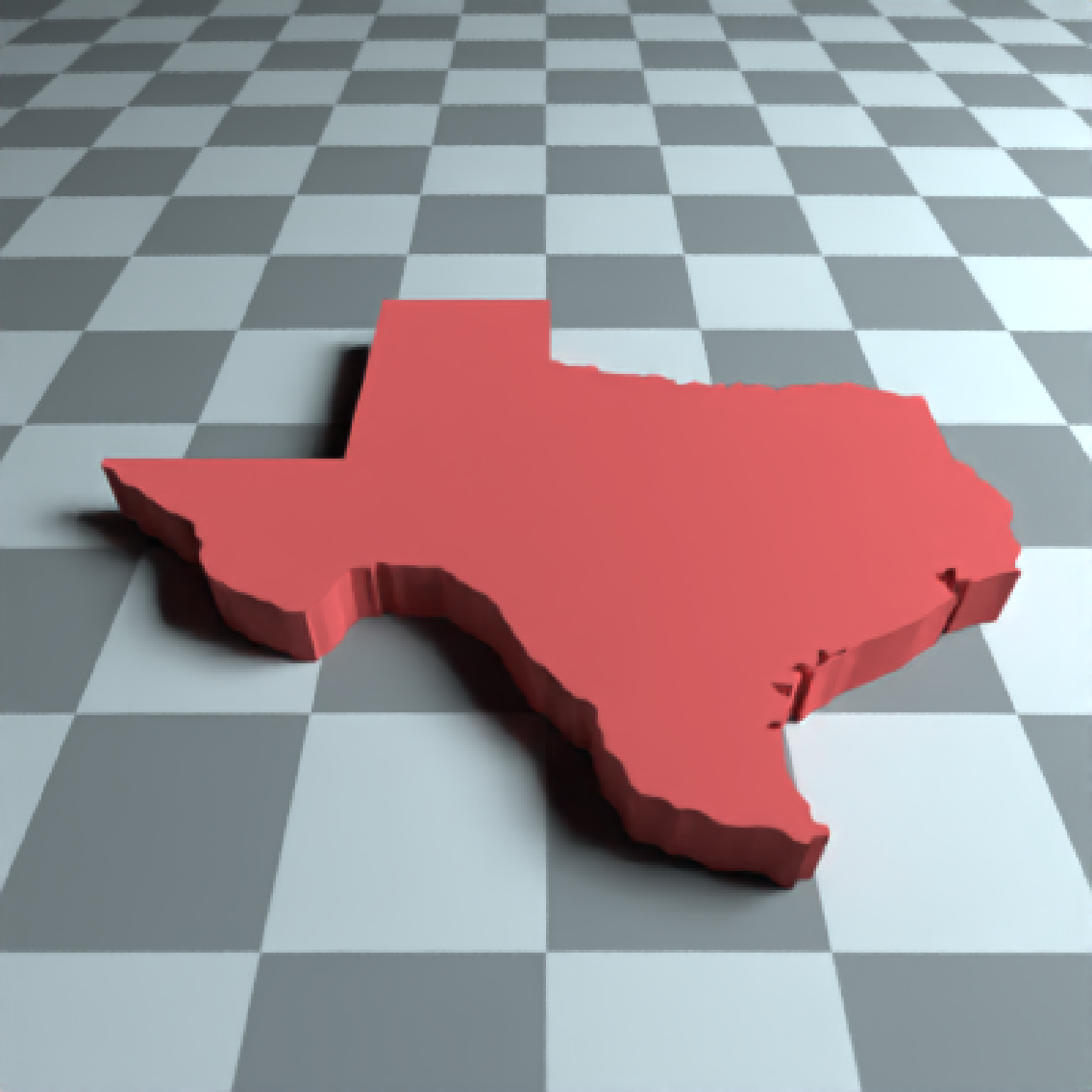
 #We can also directly pass in sf polygons:
if(run_documentation()) {
if(length(find.package("spData",quiet=TRUE)) > 0) {
us_states = spData::us_states
texas = us_states[us_states$NAME == "Texas",]
#Fix no sfc class in us_states geometry data
class(texas$geometry) = c("list","sfc")
}
}
#This uses the raw coordinates, unless `center = TRUE`, which centers the bounding box
#of the polygon at the origin.
if(run_documentation()) {
generate_ground(depth=-0.01,
material = diffuse(color="grey50",checkercolor="grey20")) %>%
add_object(extruded_polygon(texas, center = TRUE,
material=diffuse(color="#ff2222",sigma=90))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=30,x=-30,radius=10,
material=light(color="lightblue",intensity=40))) %>%
render_scene(parallel=TRUE,lookfrom = c(0,10,-10),samples=16,fov=60)
}
#We can also directly pass in sf polygons:
if(run_documentation()) {
if(length(find.package("spData",quiet=TRUE)) > 0) {
us_states = spData::us_states
texas = us_states[us_states$NAME == "Texas",]
#Fix no sfc class in us_states geometry data
class(texas$geometry) = c("list","sfc")
}
}
#This uses the raw coordinates, unless `center = TRUE`, which centers the bounding box
#of the polygon at the origin.
if(run_documentation()) {
generate_ground(depth=-0.01,
material = diffuse(color="grey50",checkercolor="grey20")) %>%
add_object(extruded_polygon(texas, center = TRUE,
material=diffuse(color="#ff2222",sigma=90))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=30,x=-30,radius=10,
material=light(color="lightblue",intensity=40))) %>%
render_scene(parallel=TRUE,lookfrom = c(0,10,-10),samples=16,fov=60)
}
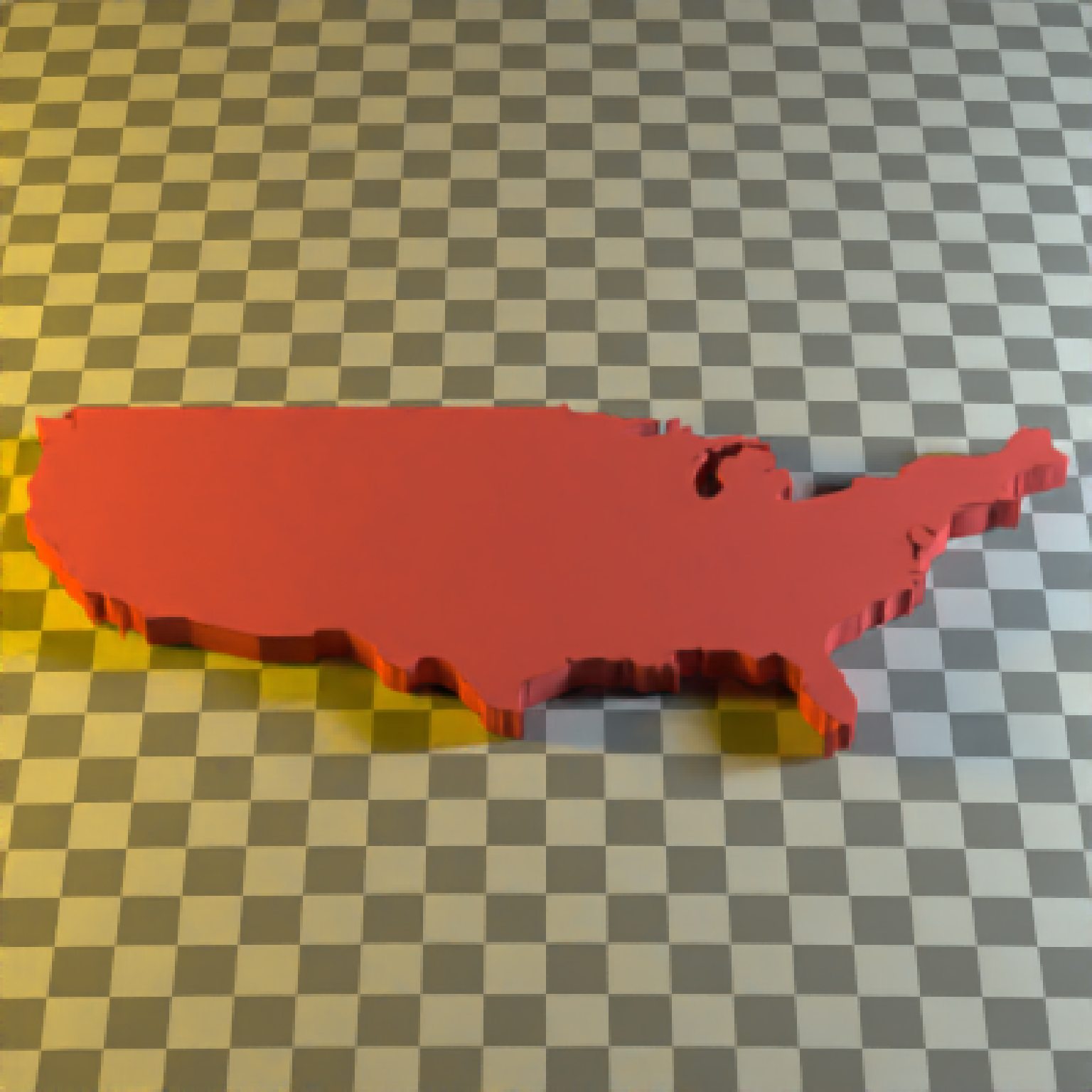
 #Here we use the raw coordinates, but offset the polygon manually.
if(run_documentation()) {
generate_ground(depth=-0.01,
material = diffuse(color="grey50",checkercolor="grey20")) %>%
add_object(extruded_polygon(us_states, x=-96,z=-40, top=2,
material=diffuse(color="#ff2222",sigma=90))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=30,x=-100,radius=10,
material=light(color="lightblue",intensity=200))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=30,x=100,radius=10,
material=light(color="orange",intensity=200))) %>%
render_scene(parallel=TRUE,lookfrom = c(0,120,-120),samples=16,fov=20)
}
#Here we use the raw coordinates, but offset the polygon manually.
if(run_documentation()) {
generate_ground(depth=-0.01,
material = diffuse(color="grey50",checkercolor="grey20")) %>%
add_object(extruded_polygon(us_states, x=-96,z=-40, top=2,
material=diffuse(color="#ff2222",sigma=90))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=30,x=-100,radius=10,
material=light(color="lightblue",intensity=200))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=30,x=100,radius=10,
material=light(color="orange",intensity=200))) %>%
render_scene(parallel=TRUE,lookfrom = c(0,120,-120),samples=16,fov=20)
}
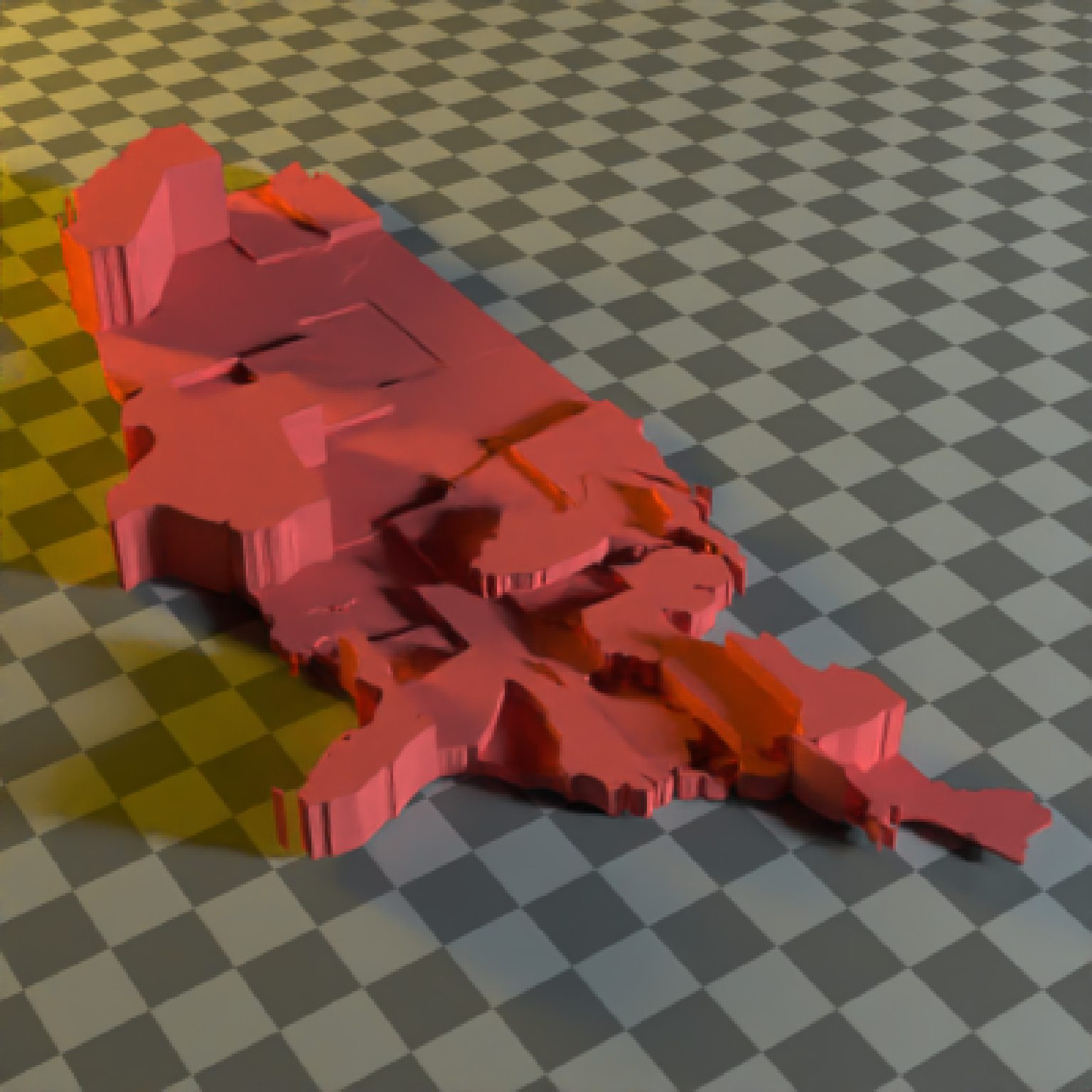
 #We can also set the map the height of each polygon to a column in the sf object,
#scaling it down by the maximum population state.
if(run_documentation()) {
generate_ground(depth=0,
material = diffuse(color="grey50",checkercolor="grey20",sigma=90)) %>%
add_object(extruded_polygon(us_states, x=-96,z=-45, data_column_top = "total_pop_15",
scale_data = 1/max(us_states$total_pop_15)*5,
material=diffuse(color="#ff2222",sigma=90))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=30,x=-100,z=60,radius=10,
material=light(color="lightblue",intensity=250))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=30,x=100,z=-60,radius=10,
material=light(color="orange",intensity=250))) %>%
render_scene(parallel=TRUE,lookfrom = c(-60,50,-40),lookat=c(0,-5,0),samples=16,fov=30)
}
#We can also set the map the height of each polygon to a column in the sf object,
#scaling it down by the maximum population state.
if(run_documentation()) {
generate_ground(depth=0,
material = diffuse(color="grey50",checkercolor="grey20",sigma=90)) %>%
add_object(extruded_polygon(us_states, x=-96,z=-45, data_column_top = "total_pop_15",
scale_data = 1/max(us_states$total_pop_15)*5,
material=diffuse(color="#ff2222",sigma=90))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=30,x=-100,z=60,radius=10,
material=light(color="lightblue",intensity=250))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=30,x=100,z=-60,radius=10,
material=light(color="orange",intensity=250))) %>%
render_scene(parallel=TRUE,lookfrom = c(-60,50,-40),lookat=c(0,-5,0),samples=16,fov=30)
}
